Introduction️
NXDN (Next Generation Digital Narrowband) is a digital radio standard developed jointly by Icom and Kenwood in Japan. It was designed for voice and data communications in bidirectional radio environments, such as mobile and portable radio communication systems used by organizations like emergency services, companies, and government agencies.️
These communications may be sent without encryption or using DES or AES encryption as specified in the NXDN TS 1-D Version 1.3 specification NXDN TS 1-D Version 1.3. In this case we will focus on Scramble encryption, which is defined as follows.️
- The Scramble cipher is an encryption algorithm that consists of a random bit inversion through a
XORoperation at the bit level between a sequence of voice bits or other data and aPNsequence. ThePNsequence uses the polynomialP(x) = X^15 + X + 1, which has a period of repetition of 32,767 bits, and a default encryption key is used for thePNsequence. Since thePNsequence is generated by a 15-stage shift register, the encryption key can be selected from among 32,767 different keys, except for all zero keys.️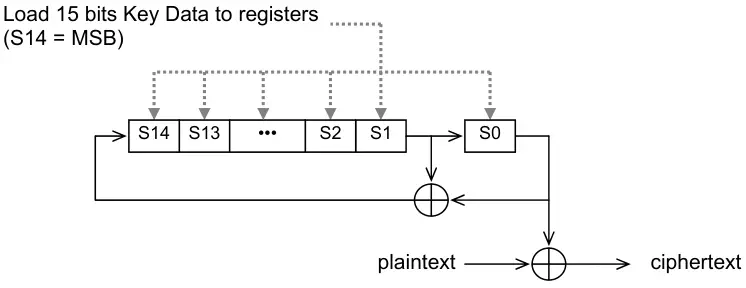 Here are the steps of the encryption process, which is a linear feedback shift register (LFSR) record.️
Here are the steps of the encryption process, which is a linear feedback shift register (LFSR) record.️
- The 15-bit encryption key bits are loaded into the registers
S14...S0 - An operation
XORis performed with registerS0and a bit from the plain-text to generate a cipher-text bit️ - An operation
XORis performed with registerS0and registerS1, calledX - The records shift to the right, passing
S14equal to X,S13equal toS14, and so on - Steps 2-4 are repeated until no more plain-text bits are to be encrypted
- The 15-bit encryption key bits are loaded into the registers
This algorithm has been implemented using the C programming language, with the function main() being configurable for the array key_15_bit with the encryption key, the array list_bits with the plain-text (or cipher-text if we want to decrypt), and the array bits_to_xor with the indices of the bits to perform the XOR operation (in this case 13 and 14 being S1 and S0). This is an example of execution for the plain-text “ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST” and the encryption key “1”, returning the encrypted text in binary.️
$ ./lfsr
NXDN-LFSR
1100000101000011010000110100001001000101010100100100011100110000010010000101101001001101001011000101100000001110001100001101000101010000010101000101010101000000
Source code️
#include <stdio.h>
int lfsr(int *register_lfsr, int *bits_to_xor, int *result, int size_register, int iterations)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < iterations)
{
// Save last bit register and XOR operation
result[i] = result[i] ^ register_lfsr[size_register - 1];
// Xor bits
int xored = register_lfsr[bits_to_xor[0]] ^ register_lfsr[bits_to_xor[1]];
// Shift bits [1,0]-->[0,1]
int prev = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < size_register; j++)
{
if (j == 0)
{
prev = register_lfsr[j];
// Save XORed bit
register_lfsr[0] = xored;
}
else if (j > 0)
{
int tmp = prev;
prev = register_lfsr[j];
register_lfsr[j] = tmp;
}
}
// Up
i++;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// Key 1 0x1
int key_15_bit[15] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1};
// Text ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRST
int list_bits[160] = {0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,
0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,
0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,
0,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,
0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0};
// Bits to XOR S1(13)^S0(14)
int bits_to_xor[2] = {13, 14};
int size_array = sizeof(list_bits)/sizeof(list_bits[0]);
lfsr(key_15_bit, bits_to_xor, list_bits, 15, size_array);
printf("NXDN-LFSR\n");
for (int i = 0; i < size_array; i++)
{
printf("%d", list_bits[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Conclusion️
As has been observed in the article, the encryption used in NXDN (Scramble) is weak since it can only use 32767 keys making it a target for attacks as in less than one second of a modern processor it can generate the decryption of an encrypted text for all keys.️